Scientific schools
The Engineering and Physical Institute is one of the largest scientific centers of NTU "KPI", and covers about 35% of all scientific activity of the university with emphasis on applied mathematics, applied physics, physical electronics and applied computer science.
The scientific and pedagogical composition of the Engineering and Physical Institute includes 33 doctors and more than 110 candidates of physical-mathematical and technical sciences, which conduct scientific research, continuing the traditions of 3 major scientific schools
It was formed in the 1930’s by Professor IM Babakov, Academician AP Filippov Corresponding Member VM Maizel and their students.
Scientific studies focus on the development of methods of mathematical modeling and computer analysis of physical processes of different nature in applied problems; development of mathematical models and algorithms of computer modeling of nonlinear behavior of new and traditional materials and systems; development of algorithms and methods in management theory, navigation; Apply computer simulation methods for forecasting and recognition.
Currently, representatives of this school work at 5 departments (dynamics and strength of machines; computer modeling of processes and systems; mechanics of solid environment and materials resistance; applied mathematics; geometric modeling and computer graphics).
It leads his history from the works of prominent scientists of the Ukrainian Physical and Technical Institute, which simultaneously worked at the Faculty of Physics and Mechanical- Academicians KD Sinelnikov, AK Walter, OI Lepunsky, IV Overtov, LD Landau and others. The founder of the school is a prominent scientist, Honored Worker of Science and Technology of Ukraine, Laureate of the State Prize, Professor, Doctor of Physical Mat. Sciences LS Palatnik.
Scientific studies are focused on the study of physical properties, mechanisms of formation of film and other nanomatic objects, phase transformations in condensed systems, behavior of materials in extreme conditions of cosmic, nuclear and thermonuclear reactors; Development of physical bases of technologies of new materials with unique properties (nanocrystalline objects, films and film compositions, fullerenes, ceramics, biomaterials, quasicristals, artificial diamonds, super -solid materials, etc.); research of film nano -size layers and layered heterosystems based on semiconductor compositions that provide the work of modern electronics and solar energy products; electron microscopy, study of structural defects and physical properties of thin films, thermoelectric material science.
Currently, representatives of this school work at 3 departments: metals and semiconductors, physical materials for electronics and helionergy and the Department of Physics.
The founding of the studies of the ionosphere in the CPI is associated with the figure of S. Ya. Braude and the production in 1952 – 1954. To deepen ionospheric research in 1963 was organized the Ionosphere Research Laboratory (Head of Prof. VI Taran). For the study of the ionosphere by the method of non-coherent scattering of radio waves in the 1960s-1980s, a complex of non-coherent scattering of a meter-wave radio wave with a ground wave with a terrestrial double-dioxide parabolic antenna with a diameter 25 m, a complex of decimeter wavelength with frequency -glass -anntane and a shortwave heating stand. This complex, recognized as the object of the national heritage of Ukraine, is unique to the middle latitudes of Europe.
Research is conducted today at the Radio Electronics Department together with Institute of Ionosphere of NAS of Ukraine.
Topics and directions of applied research of the Scientific School "Mechanics and Applied Mathematics"
Reduction of the large amplitude resonance dynamics of the systems with limited power supply
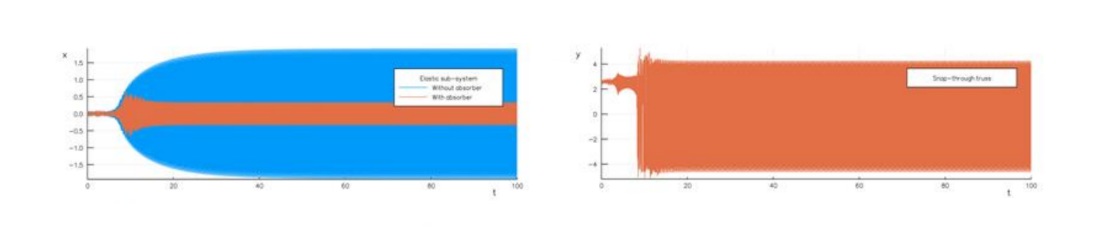
The systems with limited power supply (or non-ideal systems, or NIS) are characterized by interaction of source of energy and the elastic sub-system. The most interesting phenomenon here is the Sommerfeld effect, when the large amplitude resonance regime of the elastic sub-system is observed, and a big part of the source energy is leaved to the resonance vibrations. A use of vibration absorber permits to reduce the large amplitude vibrations. It is planned to investigate dynamics of the NIS containing nonlinear absorber, such as the pendulum, Mises girder et al. Both n-DOF and distributed NIS can be considered. Modern methods of nonlinear dynamics will be used in this investigation.
 Novelty and benefits:
Novelty and benefits:
- Use of nonlinear absorbers to reduce resonance vibrations of NIS is original. Methods of analysis of the NIS nonlinear dynamics are original.
- It is expected a determination of the system parameter regions where a strong reduction of the vibration amplitudes can be obtained.
Outlook and perspectives. Results of the investigation of resonance dynamics and absorption of large amplitudes resonance dynamics in NIS can be used in engineering practice, in particular, in civil engineering, bridge construction, transport construction, etc.
Contact: department Applied Mathematics; supervisor of the current Scientific Direction: Prof. Yuri V. Mikhlin
Investigation of geometrically nonlinear, free and parametric vibration of the laminated and functionally-graded plates and shallow shells by meshless methods, based on R-functions theory
The basic goal of the project is creation of the universal numerically – analytical method for solving geometrically nonlinear static and dynamic problems of the laminated and functionally graded plates and shallow shells theory with complex plan form and different types of the boundary conditions. The proposed method will be based on the application of the R-functions theory and variational method.
Novelty and benefits:
- a new mathematical approach which allows to present problem solution in analytical form. Created the software in order to solve geometrically nonlinear bending problems of a finding natural frequencies of vibrations of multilayered and functionally-graded plates and shallow shells of the any form in the plan;
- developed algorithms of research of geometrically nonlinear vibrations of laminated functionally-graded plates and shallow shells with complex planform;
- new approach to investigation parametric vibration of the laminated functionally graded plates with various kinds of boundary conditions and different geometric form.
Outlook and perspectives. New theoretical and numerical results will increase scientific knowledge in order to research parametric vibration, buckling problem, bending and finding frequencies of free vibration of composite laminated and sandwich panels and plates of an arbitrary form. These elements are widely applied in different field of industry, particularly, in aero-space, building manufacturers.
Contact: department Applied Mathematics, supervisor of the current ScientificDirection: Prof. Lidiya V. Kurpa
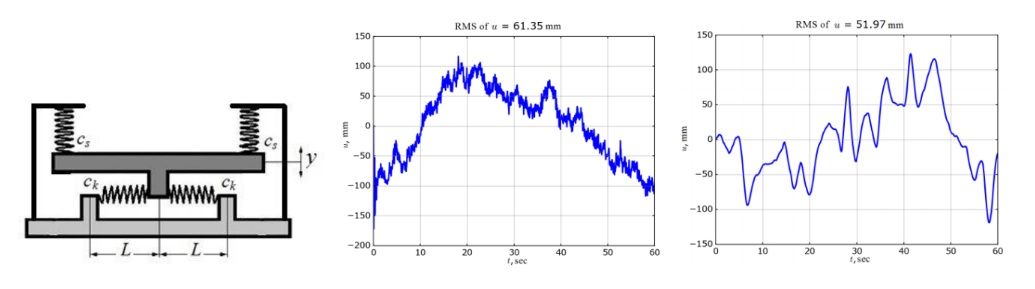
Stochastic dynamics of the vibrational isolation systems with nonlinear suspension
At the present-day engineering practice, nonlinear stiffness or damping suspension is widely used for the reduction of the vibrations. A special attention here should be made on the systems with a quasi-zero stiffness because they can provide a vibro-
isolation effect together with the efficiency of usage and compact size. This work deals with the theoretical modelling and experimental observations of the vertical dynamics of a cargo platform with the quasi-zero stiffness suspension under the operational random load. A discrete non-linear computational model has been developed and analysed within numerical simulations of the random vibrations. Dynamics of the system is analysed under a kinematic stochastic wide-band stationary load. A good comparative agreement is found between the numerical simulations and experimental data.
Outlook and perspectives:
- Analysis of the transient behaviour of the nonlinear vibration of such a system
- Development of the semi-active adaptive nonlinear suspension and the algorithm of its control
- Development of the genetic algorithms of optimal designing of the parameters of the nonlinear elastic and damping elements of a vibrational isolation suspension
Contact: Dynamics and Strength of Machines Department, supervisor of the current Scientific Direction Prof. Oleksiy Larin.
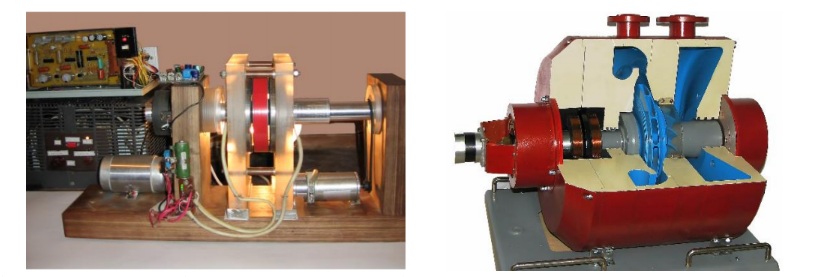
Full combined magnetic suspension of shafts and rotors in passive and active magnetic bearings
Creating a method for constructing complete magnetic suspensions of shafts and rotors of various systems and machines. Development of new types of passive and active magnetic bearings based on a refined mathematical modeling for a calculation of force and stiffness characteristics, taking into account the laws and algorithms of the control. An introduction of passive-active magnetic suspensions for various systems and machines on a basis of carrying out various phenomena of the dynamics of rotors in magnetic bearings, considering a nonlinear interconnection of electrical, magnetic and mechanical processes.
Novelty and benefits:
- The use of passive magnetic bearings on ring permanent magnets for an
organization of a more competitive full passive-active magnetic suspension. - Practical testing of new types of passive magnetic bearings based on an
application of the technique of an optimal search for parameters of a system. - Computer simulation of rotor dynamic with passive and active magnetic.
Outlook and perspectives. Creating the new types of active and passive magnetic bearings with a development of design solutions, laws, algorithms and control systems. A new type of passive magnetic bearings with a short-term variable stiffness to create competitive full passive-active magnetic suspensions.
Contact: Dynamics and Strength of Machines Department, supervisor of the current Scientific Direction: Prof. Martynenko Gennadii.
Forced nonlinear vibrations of turbine blades package with dynamic contact in the shroud
Failures caused by the increased vibrations are widespread possible breakdowns occurring in steam and gas turbines. The blades assemblies are the most dynamically loaded units of the turbines. Inter-blades detachable joints are typically used for long blades stiffness magnification. Dynamic and strength characteristics of these designs essentially depend on the contact interacting peculiarities in such bandage. Vibrations of the blades assembly become nonlinear under dynamic contact in the bandage and can be accompanied by the great number of the various phenomena. The work deals with the investigation of the forced nonlinear vibrations of blades package of turbine, taking into account the contact interaction in the shroud.
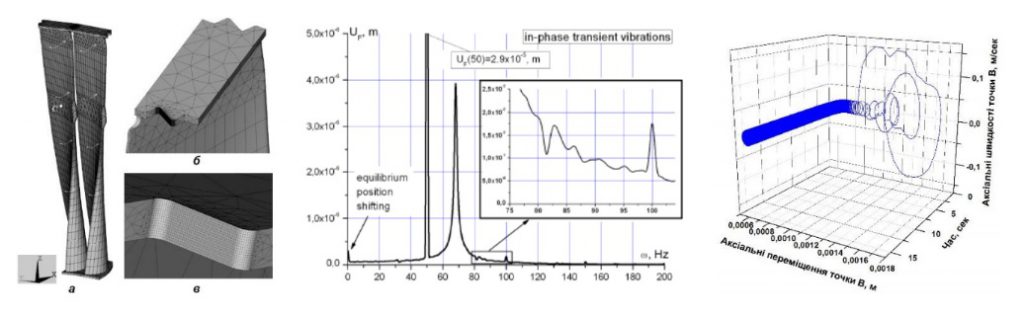
Novelty and benefits. Analysis of the nonlinear dynamics phenomena in resonance and nonresponse regimes (a changing of resonance zones, sub and super harmonics, shifting of the system stability zone etc.).
Outlook and perspectives:
1) Analysis of the process of shroud contact surfaces wear and bladed disks vibrational reliability;
2) Analysis of the nonlinear dynamics of the turbine blades taken into account a mistuning phenomenon.
Contact: Dynamics and Strength of Machines Department, supervisor of the current Scientific Direction Prof. Oleksiy Larin
Mathematical modeling and computer analysis of physical processes of different nature in applied tasks (Prof. Breslavsky D.V., Prof. Larin O.O., Prof. Lviv G.I., Prof. Simon E.A.)
Numerical modelling and software development for creep-damage processes in structural elements
Numerical modelling of creep and damage accumulation processes in structural elements and devices, which are subjected by complex action of cyclic loading and heating, can be done by use of developed software which include FEM programs for 2d, 3d problems and thin shells of revolution. Non-stationary heat expansion 3d problem is solved additionally. Original pre- and postprocessors are available.
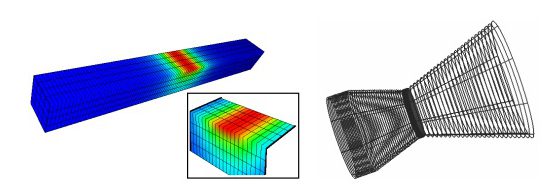
Novelty and benefits. The developed approach for cyclic loading and heating in creep-damage conditions has been presented and published in scientific journals. One part of the project was awarded by CEGB prize (UK). Developed software was used for design and long term strength analysis of different structural elements and devices of turbines as well as space- and aircrafts.
Outlook and perspectives:
- Development of new commercial version of software
- Joint projects directed to estimation of long term strength of structural elements
Contact: departments of Theoretical Mechanics, Computer Modelling of Processes and Systems; supervisors of the current Scientific Direction: Prof. D.Breslavsky, Prof O.Morachkovsky
Probabilistic modeling of structural failures for a prediction of mechanical engineering elements reliability
The work deals with a problem of the development of computational methods of determination of mechanical engineering elements life-time with random material characteristics and load. It is offered improved probabilistic models of the fatigue damage accumulation in the materials under cyclic deformation with finite strain amplitudes in the framework of continuum damage mechanics. The appropriate models take into account a random scatter of the material fatigue resistance characteristics, along with simultaneous passing of stochastic processes of material properties degradation caused by natural aging. The approaches are developed for the determination of the probability characteristics of the machine elements fatigue damage and lifetime considering the presence of possible operational random variation of the characteristics of the deformed state.
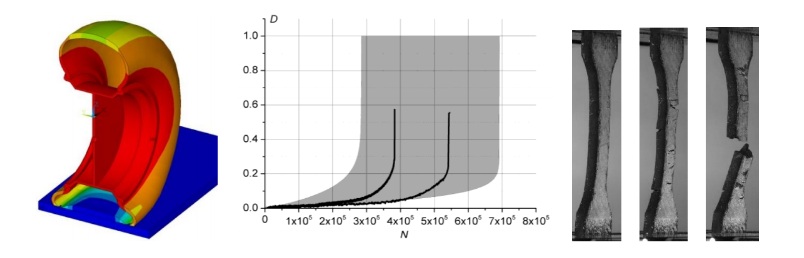
Outlook and perspectives
- Analysis of the reliability of the elastomeric materials subject to the estimation of the influence of the self-heating process (the modelling of the self-heating of the elastomeric material under the cyclic load, analysis of cyclic heating of elastomers on their aging process)
- Development of the computational approaches for the estimation of the reliability of engineering designs considering simultaneous corrosion defects stochastic growth, material chemical degradation and the process fatigue accumulation
Contact: department Dynamics and Strength of Machines; supervisor of the current Scientific Direction: Prof. Oleksiy Larin
Biomechanical computer-aided design and modeling
Theoretical (i.e. computer analysis (CAE)) of the stress state and deformation of biological bone tissues themselves and together with fixing system or implants require the development of complicated mathematical models. The main challenges here are following: complicated 3D geometry of the bone; multilayered internal structure; curvilinear orthotropy of the properties; nonlinearity of the mechanical behaviour; identification of material properties for a living tissue; specificity of the properties, geometry and loads from patient to patient; and implementation of new bio-neutral composite, functional and smart materials.
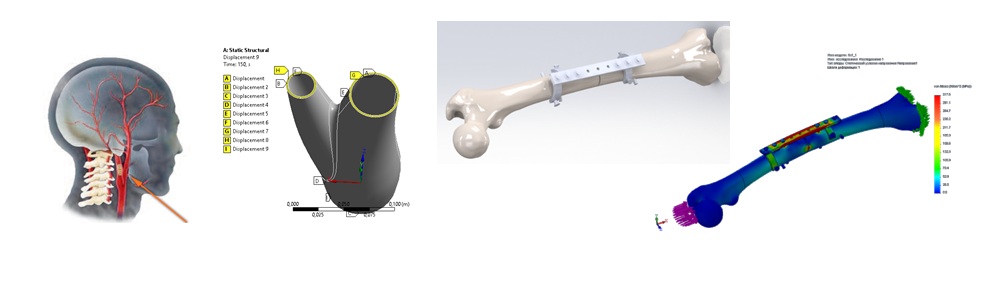 Outlook and perspectives
Outlook and perspectives
- the methods for parametric modeling of fixation devices and their installation based on computer tomography data that will enable adaptation to specific clinical cases;
- new rheological models of materials reflected the heterogeneity of bone structure, anisotropy of mechanical properties.
- automated software systems oriented on general usage of computer-aided design in medical practice by a staff of clinical centers orthopedics and traumatology
Contact: department Dynamics and Strength of Machines; supervisor of the current Scientific Direction: Prof. Gennadiy Lvov, Prof. Oleksiy Larin.
Computational analysis and synthesis of complex materials (Prof. Lviv G.I., docent Vodka O.O.)
Development of methods for designing functional anisotropic composite materials
Composite materials are widely used in various fields of modern technology due to the fact that their physical and mechanical properties allow to significantly improving the technical characteristics of products. A distinctive feature of technological processes of manufacturing elements of structures from composites is the simultaneity of creating a material and a product. The change in the structure of the reinforcement makes it possible to change in the desired direction the anisotropy parameters of the stiffness, strength, and thermal-physical properties of the composite materials.
The control of anisotropy of complex modules of polymer composite materials will increase the vibrational stability of structures and create effective noise absorbing materials. The creation of new materials with a given anisotropy of the properties of heat conductivity is necessary to improve the thermal insulation coatings of buildings and structures.
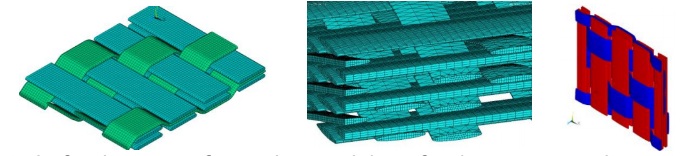
Novelty and benefits. New methods is being created for designing composite materials with the required parameters for the anisotropy of physical properties based on the combined use of numerical methods for analyzing the stressed state of structural elements and numerical methods for homogenization of composites.
Outlook and perspectives. The design of composites with the required anisotropy of mechanical properties is actualy in the manufacture of industrial wind turbine blades, elements of aircraft and space engineering structures. The creation of new materials with a given anisotropy of the properties of heat conductivity is necessary to improve the
thermal insulation coatings of buildings and structures.
Contact: department Dynamics and Strength of Machines, supervisor of the current Scientific Direction: Prof. Gennadiy Lvov.
IT for the analysis and synthesis of the structure of new materials for prediction of their physical properties
Modeling the mechanical behavior of materials at the micro level allows predicting the properties of the material at the macro level. This allows to significantly reducing the cost of testing, which is necessary to determine the mechanical properties. This is especially true for high cycle fatigue and creep testing. Computer simulation and modern information technologies allow virtually generate microstructures of materials and analyze their mechanical behavior. The most popular ways to virtually generate microstructures are the methods of cellular automata and the Voronoi tessellation. On the other hand, an important direction is the analysis of already existing microstructures and their properties.
Outlook and perspectives. Today, work is being done on the modeling of simple materials; in the future, new, complex materials are of great interest.
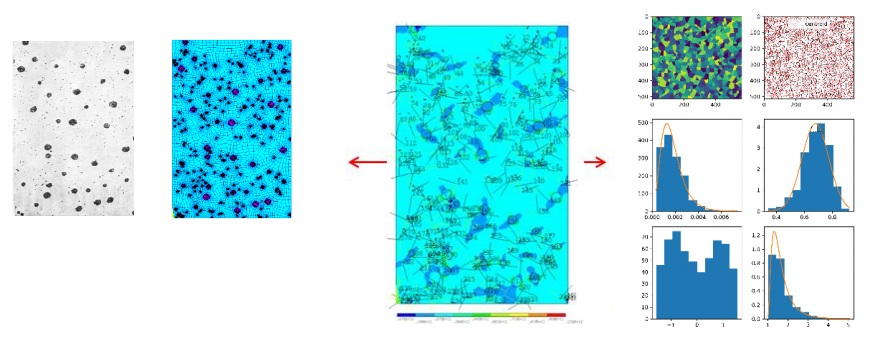
Contact: department Dynamics and Strength of Machines, supervisor of the current Scientific Direction: Dr. Oleksii Vodka
Image microstructure estimation algorithm of heterogeneous materials for identification their chemical composition
Main objective — convolutional neural network (CNN) creation for definition of heterogeneous materials chemical composition: to create the database of images and percentage of the chemical elements corresponding to material; to develop an image recognition algorithm through programming of neural network; to estimate the received system.
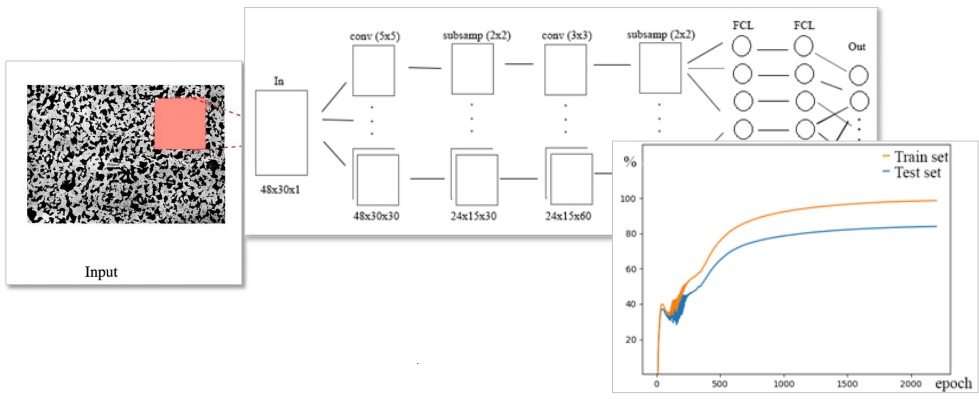
Outlook and perspectives. Today, work is being done on the modeling of simple materials; in the future, new, complex materials are of great interest.
Contact: department Dynamics and Strength of Machines, supervisor of the current Scientific Direction: Dr. Oleksii Vodka
Development of navigation, management and control systems (Professor Uspenskyi V.B., Professor Andreev Y.M., Professor Kortunov V.I.)
Development of methods, algorithms and attitude control systems of artificial earth satellites
The attitude control system of the artificial Earth satellite incorporates measuring
instruments and actuators of various types. For such systems there is experience of
development:
- high-precision algorithms of orientation determination by use of the measurements of gyroscopes; technique of their efficiency assessment;
- calculation of the optimal configuration of quantitatively redundant system of actuators: gyrodynes, inertial flywheels;
- onboard algorithms of high-precision control of the artificial satellite reorientation for remote sensing of Earth with randomly specified boundary conditions and essential elastic structural elements ;
- algorithms of rational control of the redundant systems of gyrodynes or inertial flywheels;
- optimal unloading of the gyrodyne system or inertial flywheels with the help of gas-reactive engines;
- fault tolerance of the satellite control system at emergency situations;
- modeling of thermal processes in the satellite and its onboard subsystems at orbital motion around Earth.
Novelty and benefits. The methods and algorithms were used both for control of Soviet and Ukrainian Earth satellites during last forty years and for modern systems.
Outlook and perspectives. Development of new and adaptation of existing methods and algorithms for control systems of different spacecrafts.
Contact: Department of Computer Modelling of Processes and Systems, supervisor of the current Scientific Direction: Prof. D.Breslavsky
Smart Quadcopter: Hybrid Drone for automatic monitoring, delivery of freights and safety control and security of technical objects
Our “hybrid drone” with unique “brains” navigation system is able to fly during a relatively long period of time (about 60-90 min) shipping the freight over 6 kg and due to “brains” of navigation system all proceed in autonomous mode according to a predetermined route and program of tasks. The problems our drone solves are mainly associated with agriculture: monitoring and aerial survey of forest plantations and farmland, chemical and biological treatment of agricultural land, protection and monitoring of fisheries waters. In the future it can be used in other areas, such as safety and security, search and rescue, monitoring systems etc.

Novelty and benefits
1. Payload is up to 6 kg;
2. Flight duration is up to 1.5 hours;
3. An error of coordinates determination when piloting in the presence of GNSS signals is not more than 5 m, and in the absence of GNSS signals is not more than 150 m in the first 20 minutes of flight;
4. The full functionality of the navigation system is restored in the case of GNSS signals restoring within 3 minutes.
Outlook and perspectives. Realization of our idea requires financing of a tenancy and the test platform, transportation of the quadcopter on the platform and back. Marketing services (marketing investigations, search of the companies consumers) and developing of the website with the description of product for selling, the list of services, the advertising budget, and advance of the website on the EU space.
Contact: Department of Computer Modeling of Processes and Systems, supervisor of the current Scientific Direction: prof. D.Breslavsky
Robust control of the UAV with mini autopilot
Roll channel nominal model and its uncertainties for the flight-wing UAV was found from several closed-loop flight-test data and then, a priori initial theoretical model and bounds of uncertainties were corrected and modified. Then robust control system for the roll channel was designed to increase the quality and robustness of the flight system during the system integration in the presence of uncertainties, disturbances, noise and actuator position and rate limits. It was shown that the designed robust control system can guarantee better quality for the UAV uncertain model than the PID controller in the presence of aileron angle and rate limits. Control system design is a compromise between contradictory requirements.
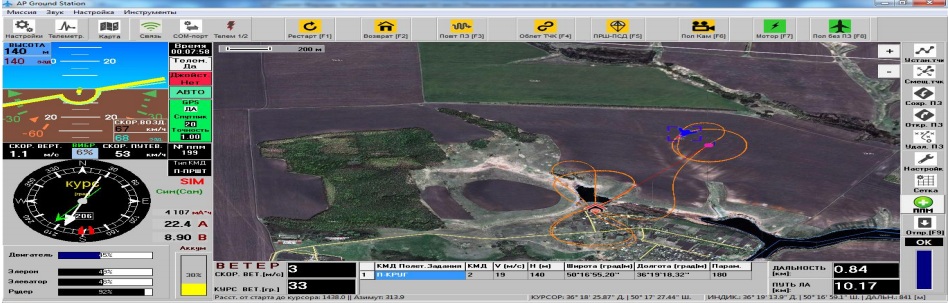
Contact: department Computer Modelling of Processes and Systems, supervisors of the current Scientific Direction: Prof. V. Kortunov
