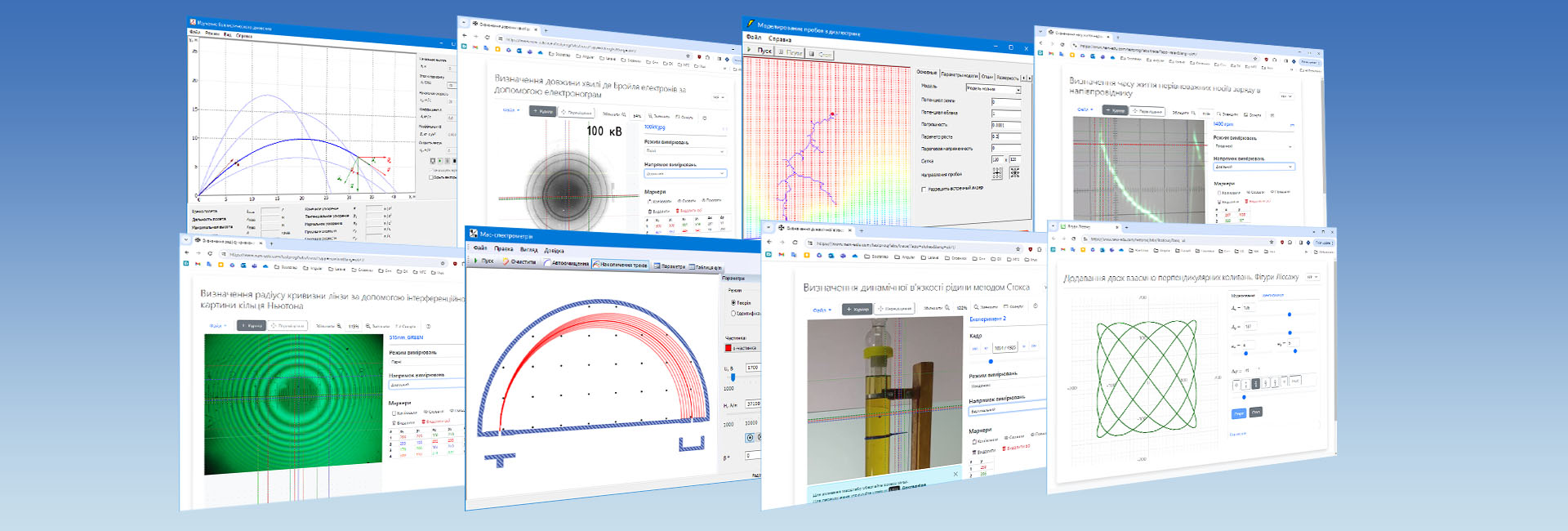
Head of the workshop – professor Synelnyk Iryna Vasylivna
Our goal
The main goal of the workshop is to introduce future engineers to the latest areas and modern methods of physical research based on the use of computer technologies in the study of various objects, processes and phenomena.
Our tasks
- Expanding the possibilities of physical laboratory workshop
- Familiarization with computer simulation as a method of physical research (the culture of building a model and conducting a computer experiment)
- Introduction to various types of simulation and different types of computer models
- Formation of the skill of using a computer to process the results of a laboratory experiment
- Study of new sections of physics: nonlinear phenomena, complex systems (self-organization, formation of structures), fractal geometry, deterministic chaos
- “Illustration” for the study of the main course of physics
List of laboratory works
Mechanics
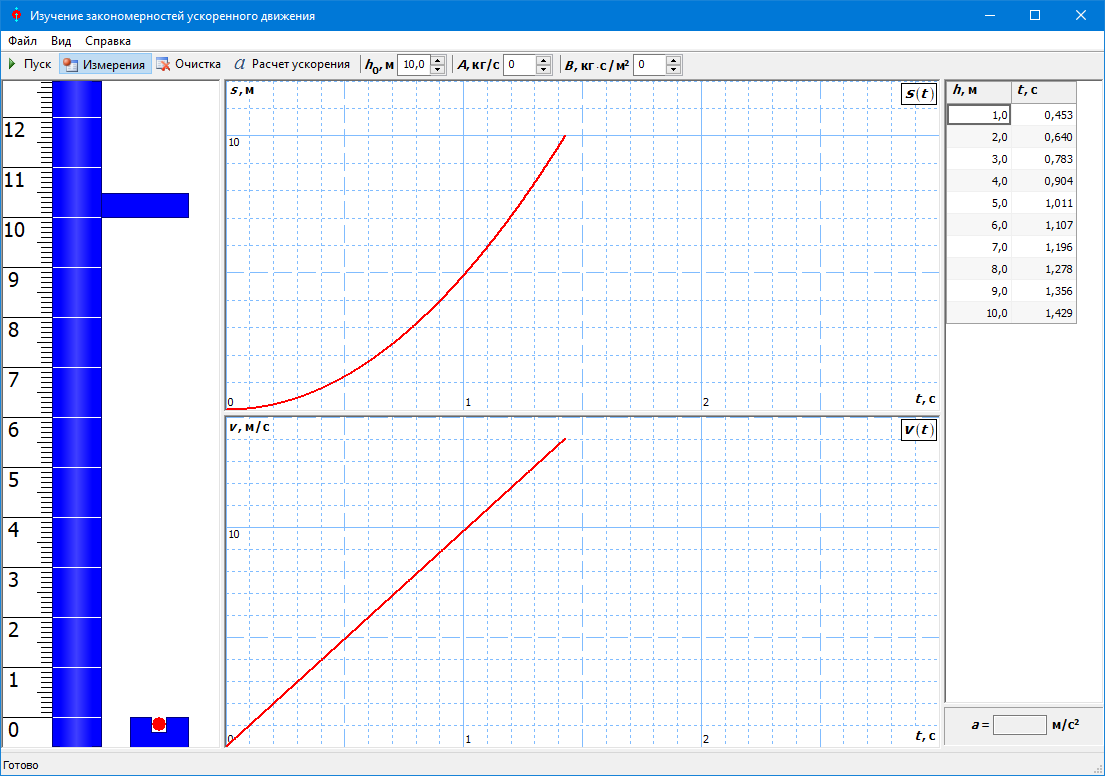
#1.1 Study of the laws of accelerated motion
Study of the laws of accelerated motion using the example of a material point moving in the Earth’s gravitational field using computer simulation.
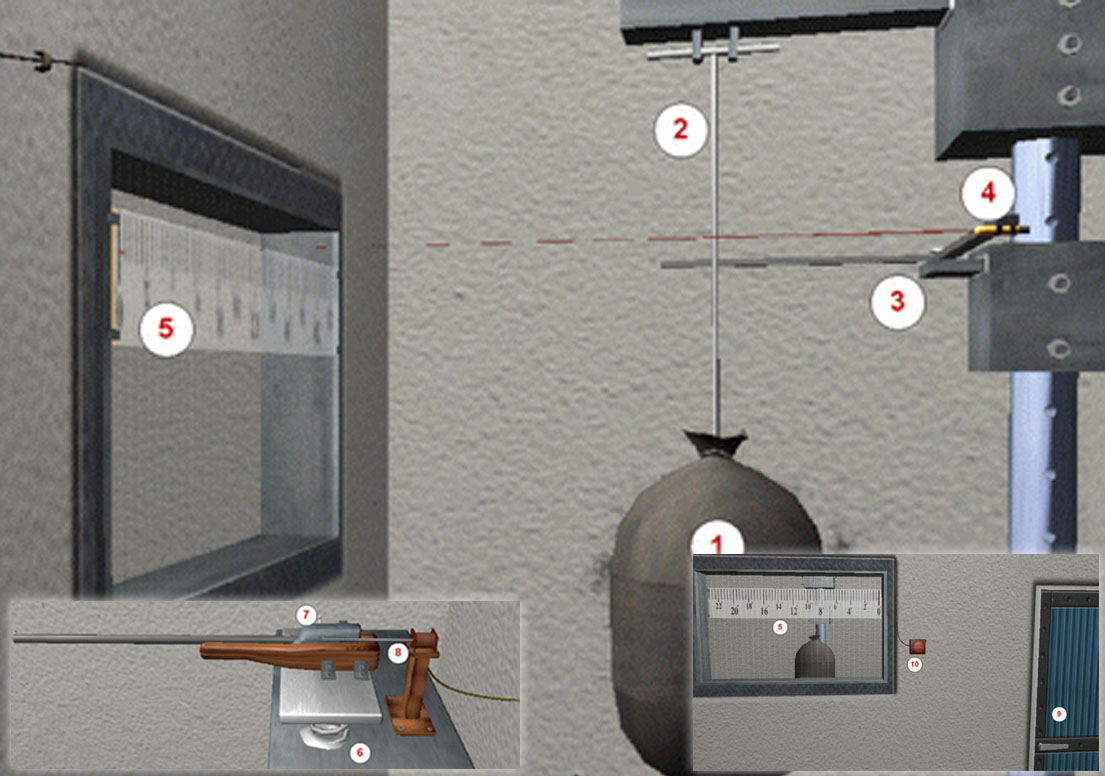
#1.2 Applying conservation laws to determine the speed of a bullet
Measuring bullet velocity using the ballistic pendulum method.
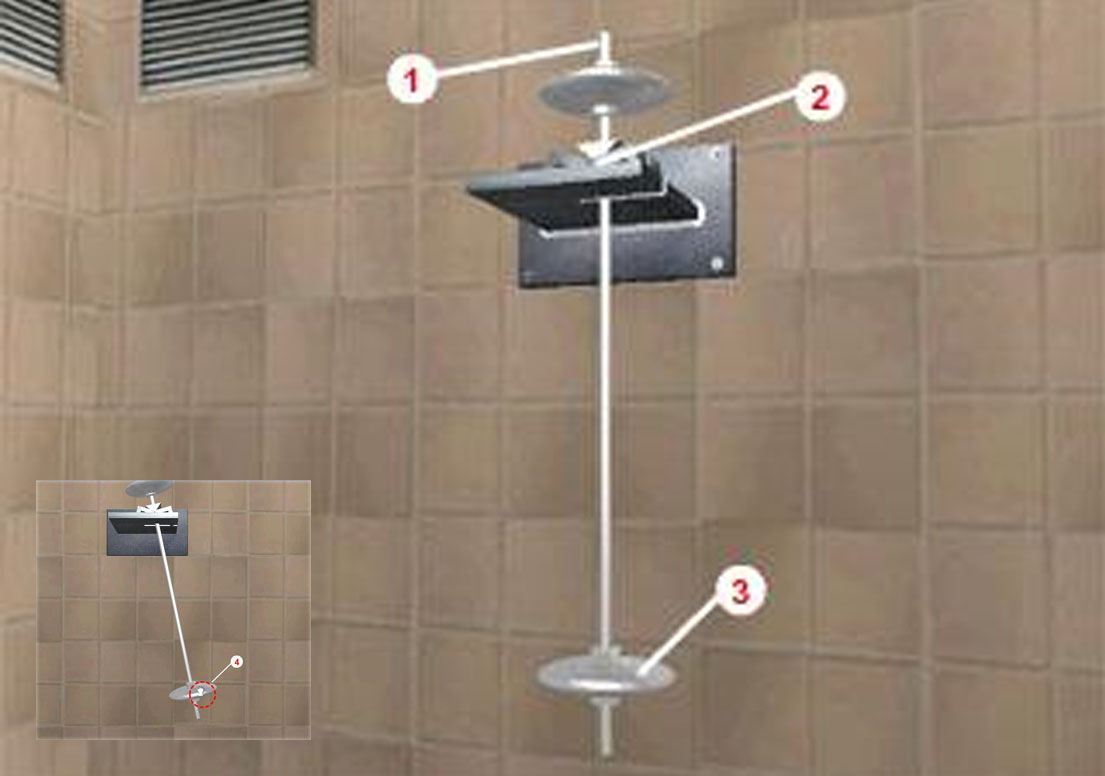

#1.3 Determining the moment of inertia of bodies of complex shape using a physical pendulum
Study of the laws of motion of a physical pendulum and experimental determination of the moment of inertia of a body of complex shape using physical pendulum.
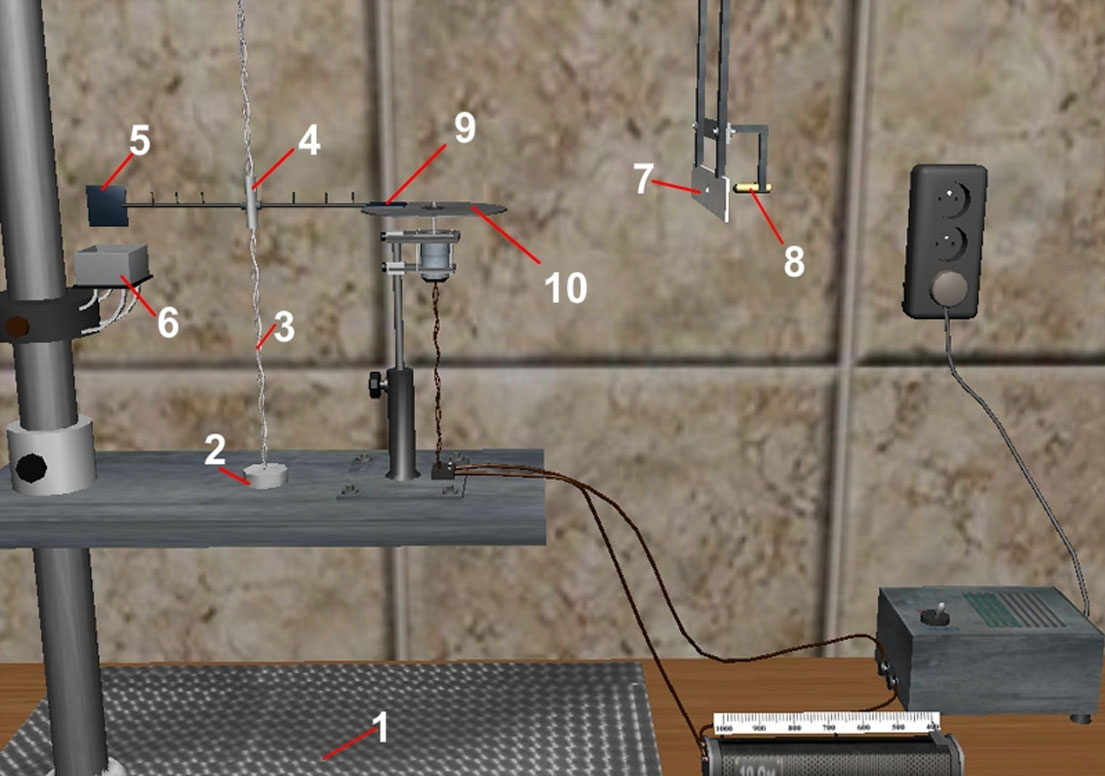
#1.4 Measuring the coefficient of viscosity of air using torsion balances
Study of the laws of viscous friction, experimental determination of the coefficient of viscosity of air using torsion balances.
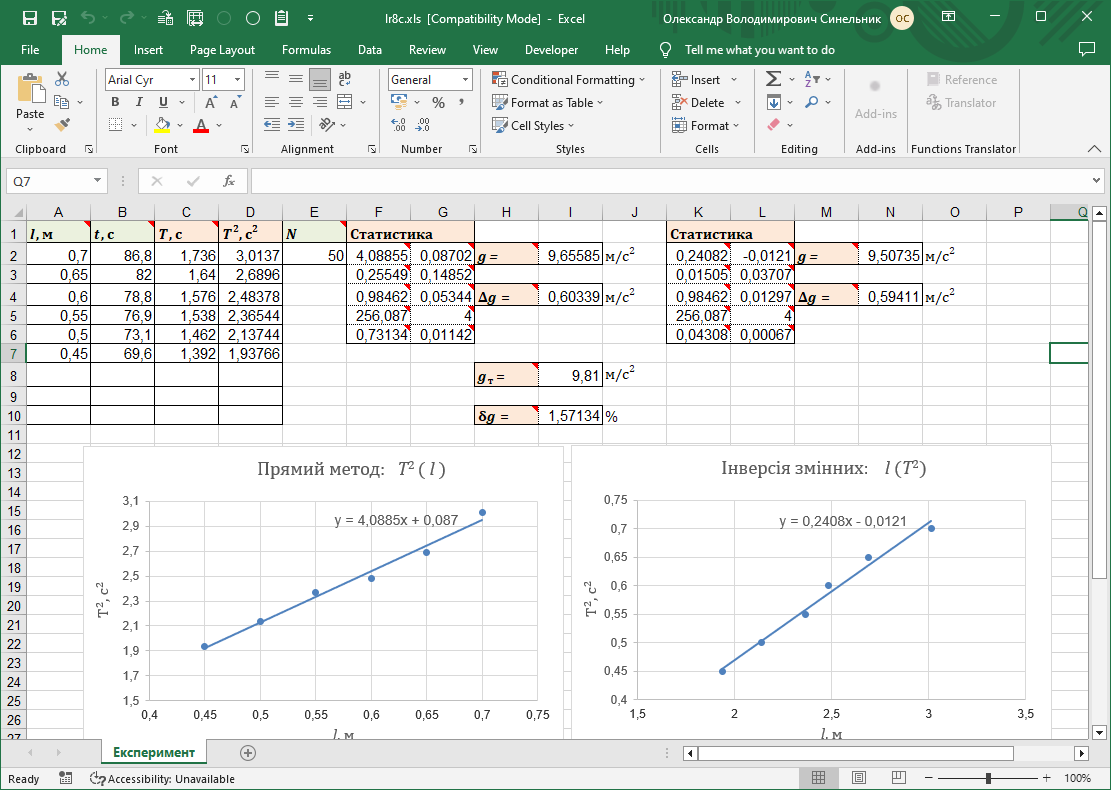
#1.9 Determining the acceleration of free fall using a mathematical pendulum
Calculation of the acceleration of free fall based on the results of a laboratory experiment using least squares method. Study of the application of the least squares method to calculate the coefficients of linear dependence.
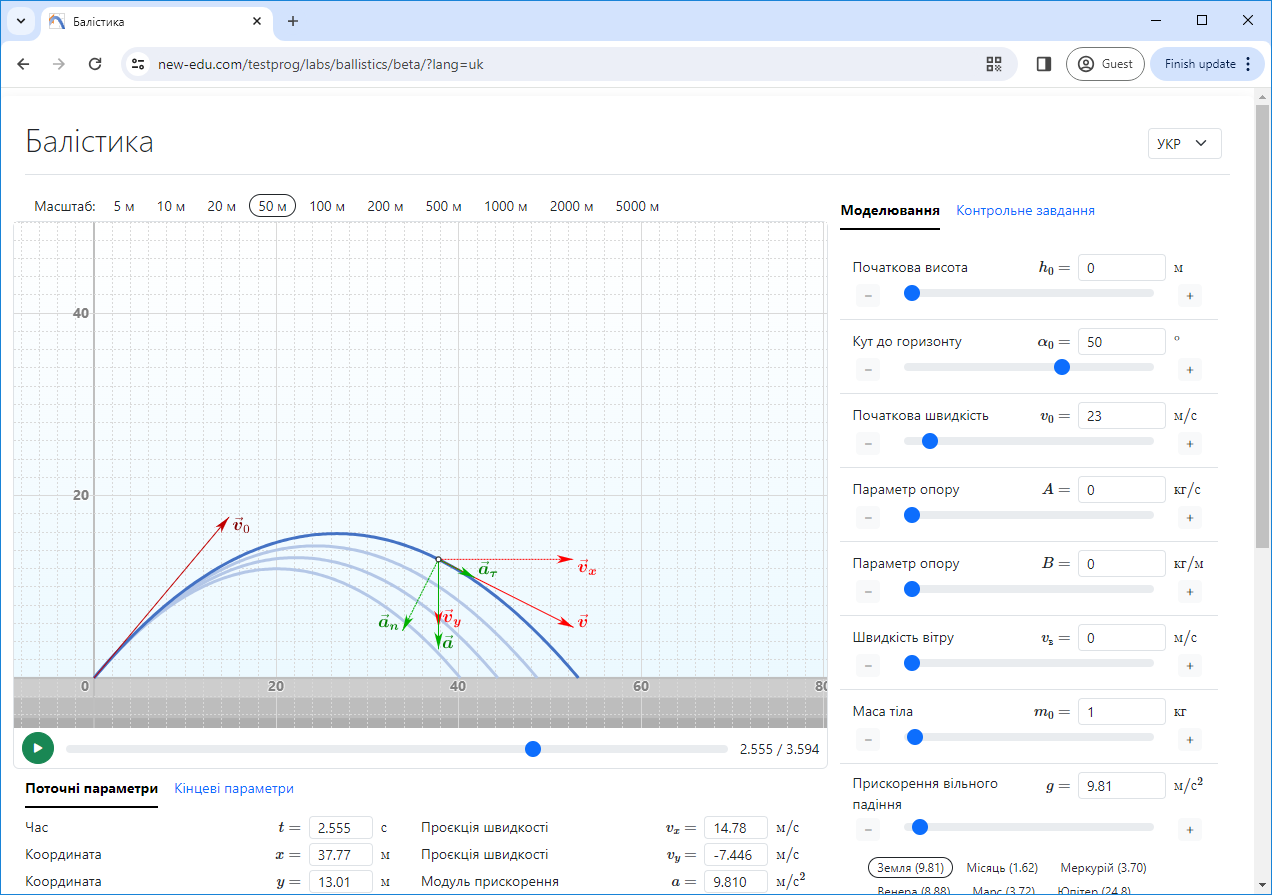
#1.10 Study of the laws of motion of a body in a gravitational field
The aim is to study the basic laws of body motion near the Earth’s surface through numerical modeling.
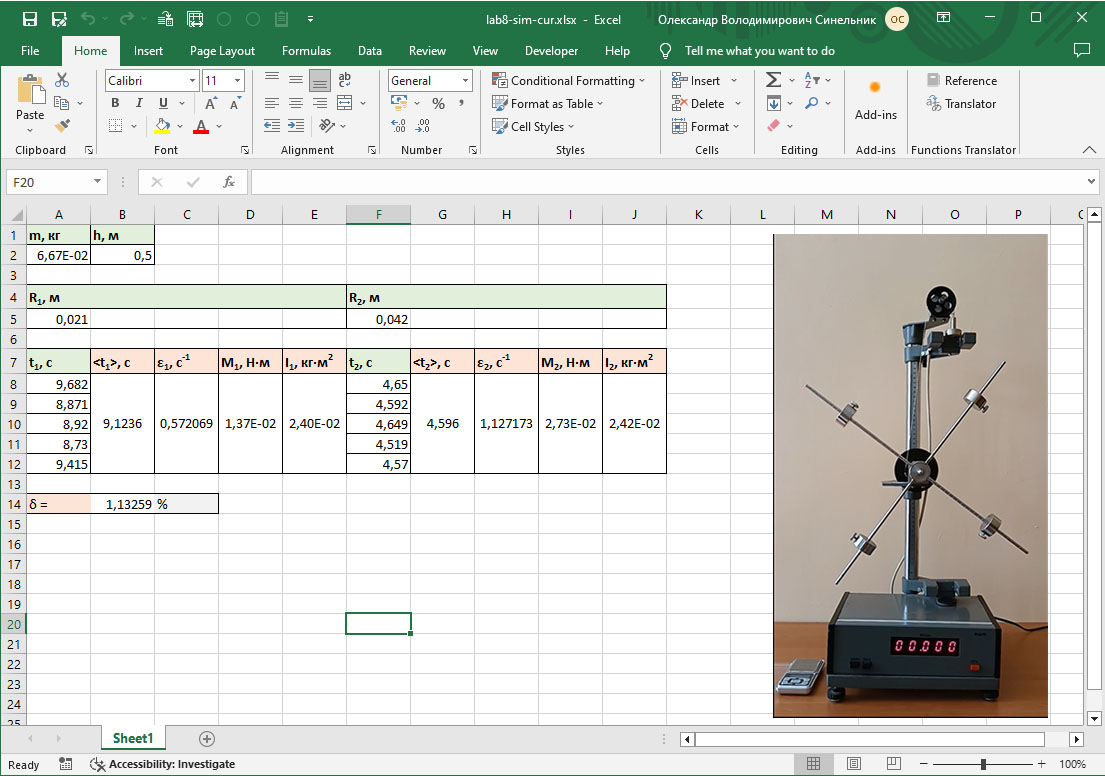
#8 Verification of the fundamental law of rotational dynamics. Processing of the experimental results
Experimental verification of the fundamental law of rotational dynamics of a solid body around a fixed axis, determination of its moment of inertia.
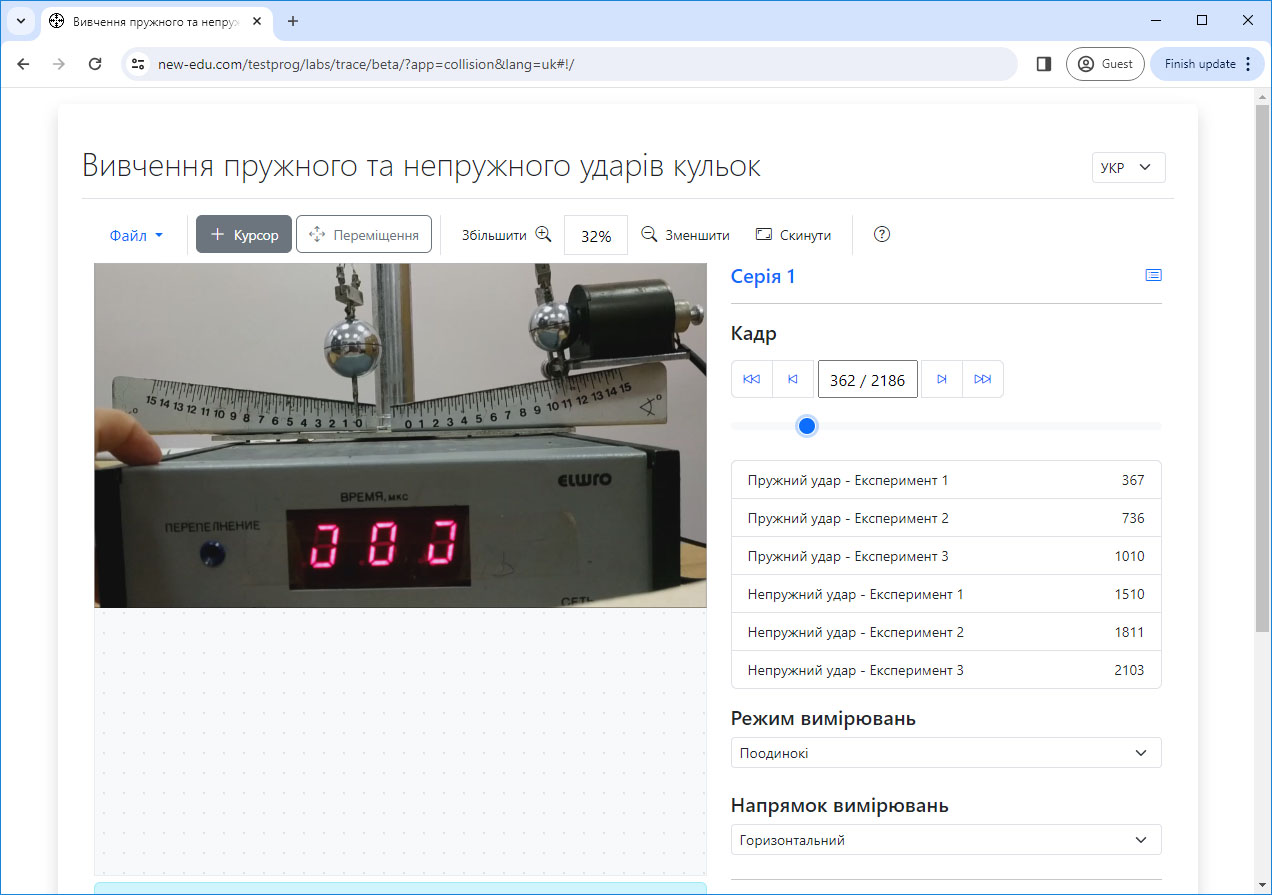
#9 Study of the laws of elastic and inelastic ball impacts
Study of elastic and inelastic collisions of bodies; experimental verification of the law of conservation of momentum using the example of elastic and inelastic collisions of two balls.
Statistical physics and thermodynamics
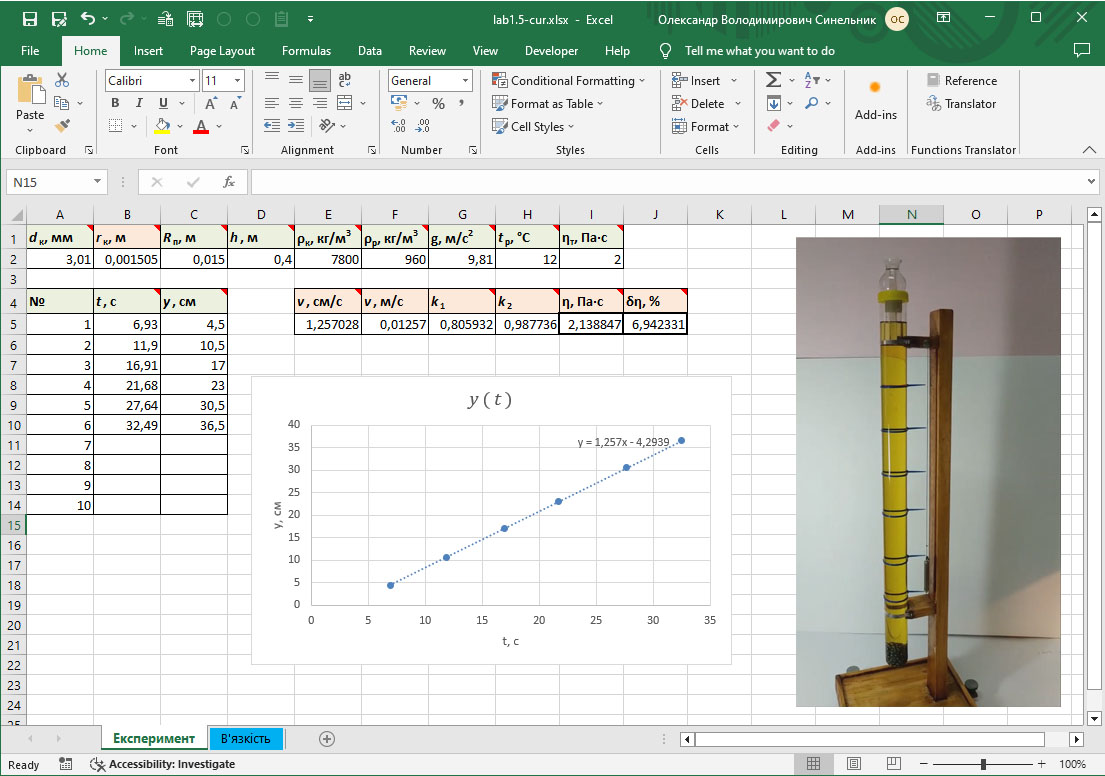
#1.5 Determination of the viscosity coefficient by the Stokes method. Processing of the experimental results
Study of the laws of motion of a spherical body in a viscous fluid; determination of the coefficient of dynamic viscosity of a fluid using the Stokes method.
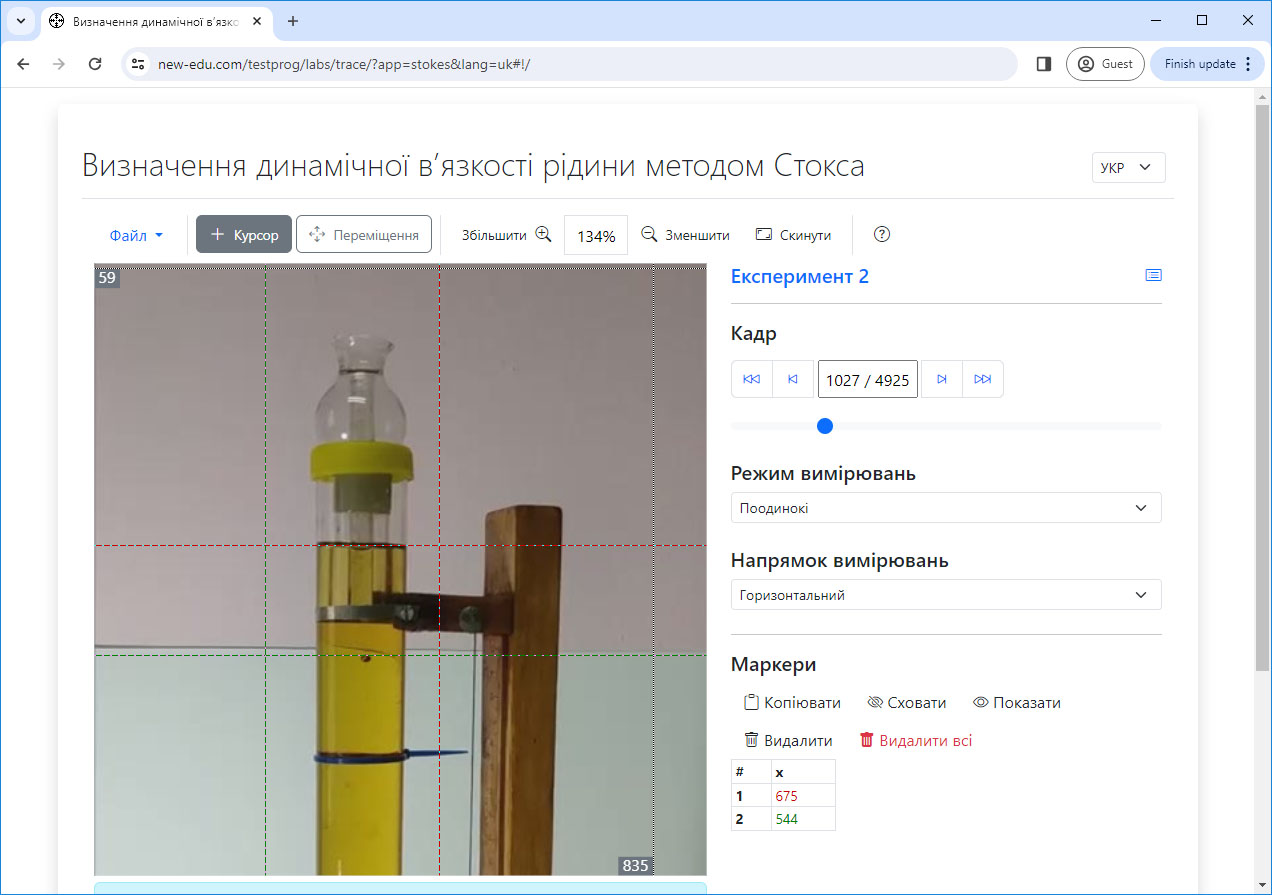
#1.5 Determination of viscosity coefficient by Stokes method. Processing of the video recording
Study of the laws of motion of a spherical body in a viscous fluid; determination of the coefficient of dynamic viscosity of a fluid using the Stokes method.

#1.11 Modeling the motion of a ball in a viscous fluid
Study of the motion of a small spherical body in a viscous fluid using computer modeling and selection of optimal experimental parameters for determining the viscosity of a fluid using the Stokes method.
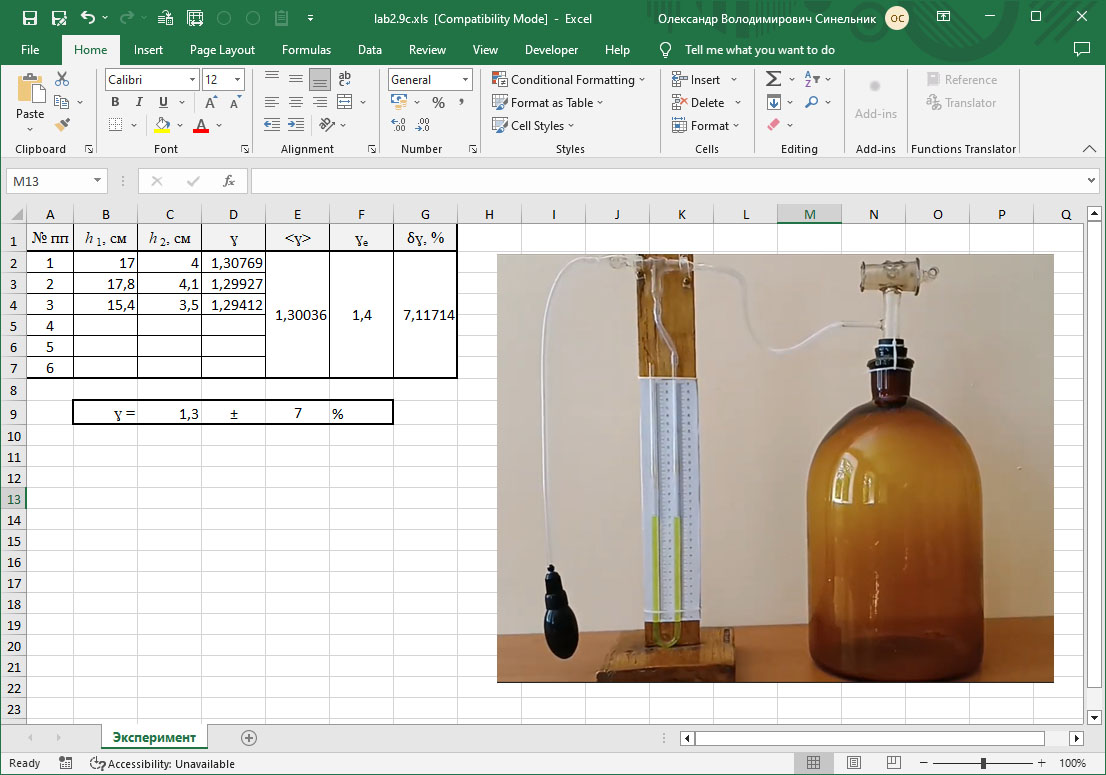
#17 Determining the ratio of molar heat capacities of gases
Experimental determination of the ratio of the molar heat capacity of a gas at constant pressure to its molar heat capacity at constant volume.
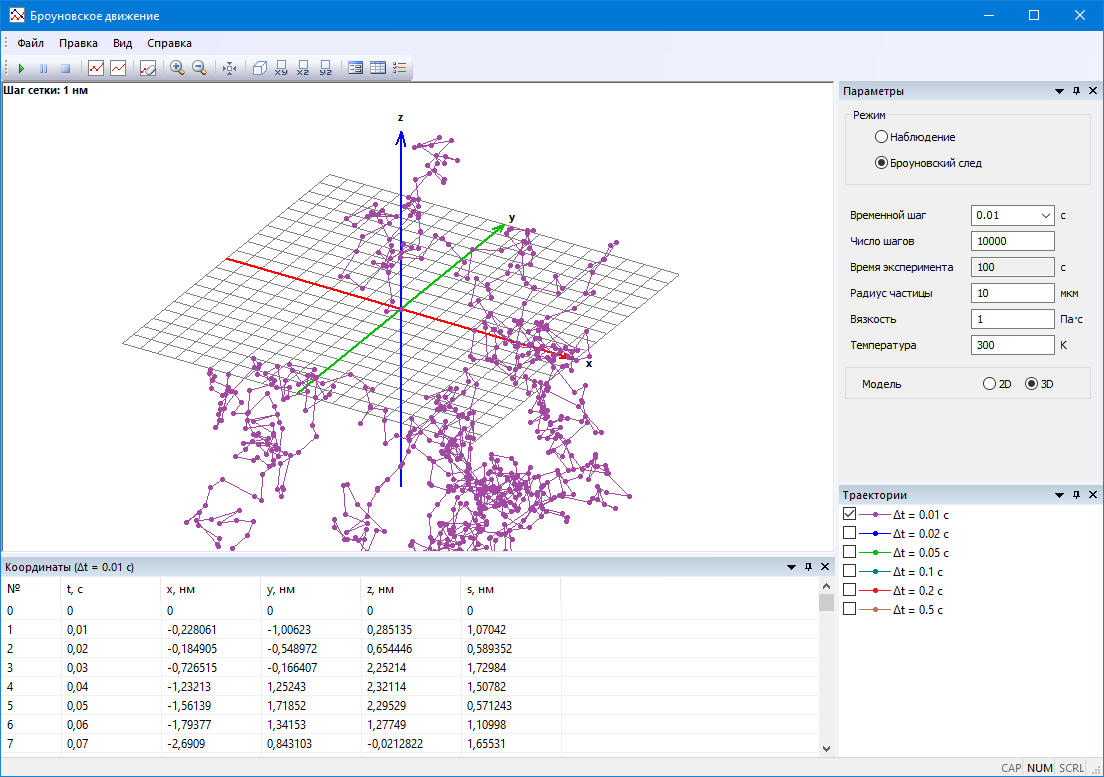
#1.13 Modeling Brownian motion
Research into the laws of Brownian motion through computer modeling, studying the laws of random motion, phenomena of self-similarity, and scale invariance.
Electricity and magnetism
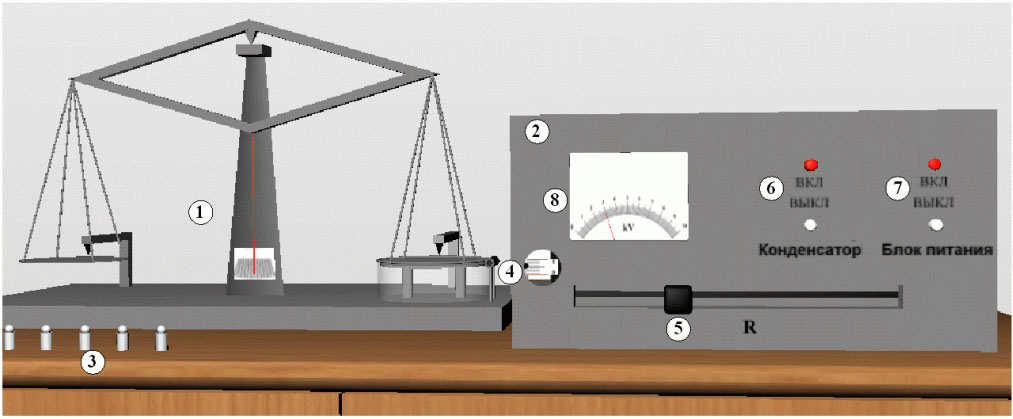
#1.6 Absolute electrometer and its application for measuring electrical constant
Familiarization with the principle of operation of an absolute electrometer, measuring the potential difference and electrical constant with it.
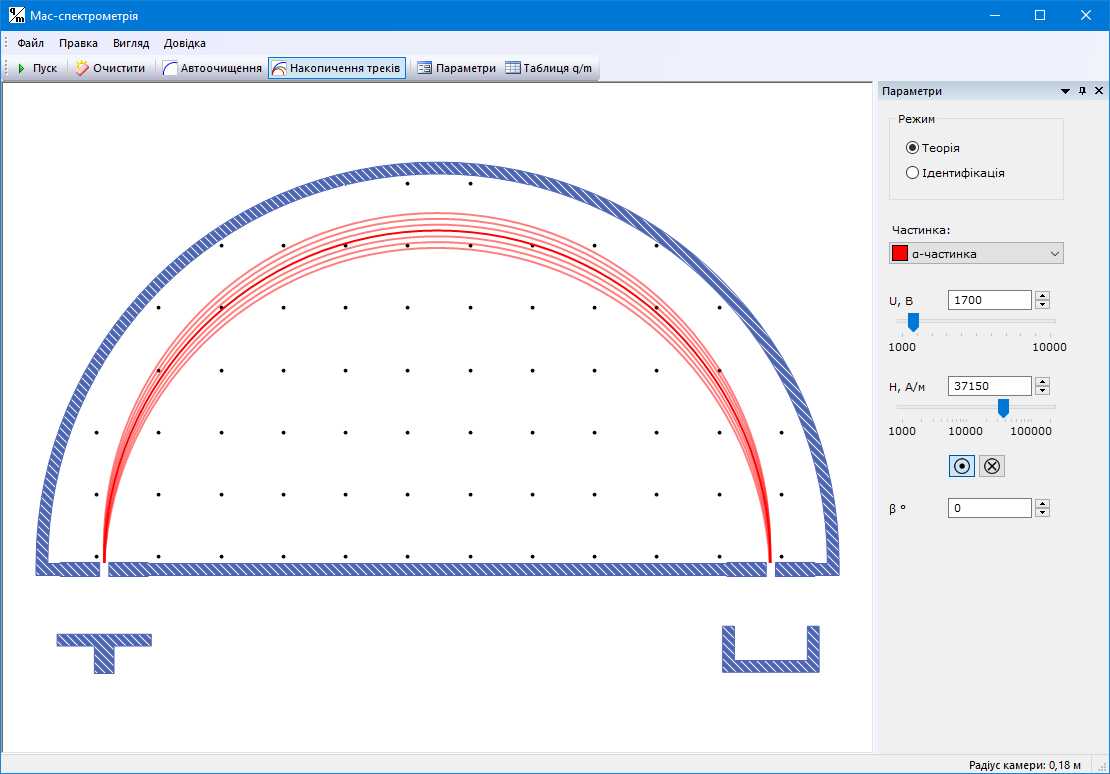
#1.7 Determination of the specific charge of a particle by mass spectrometry
Study of the physical laws underlying mass spectrometry using computer modeling; determination of the specific charge of a particle and its identification.
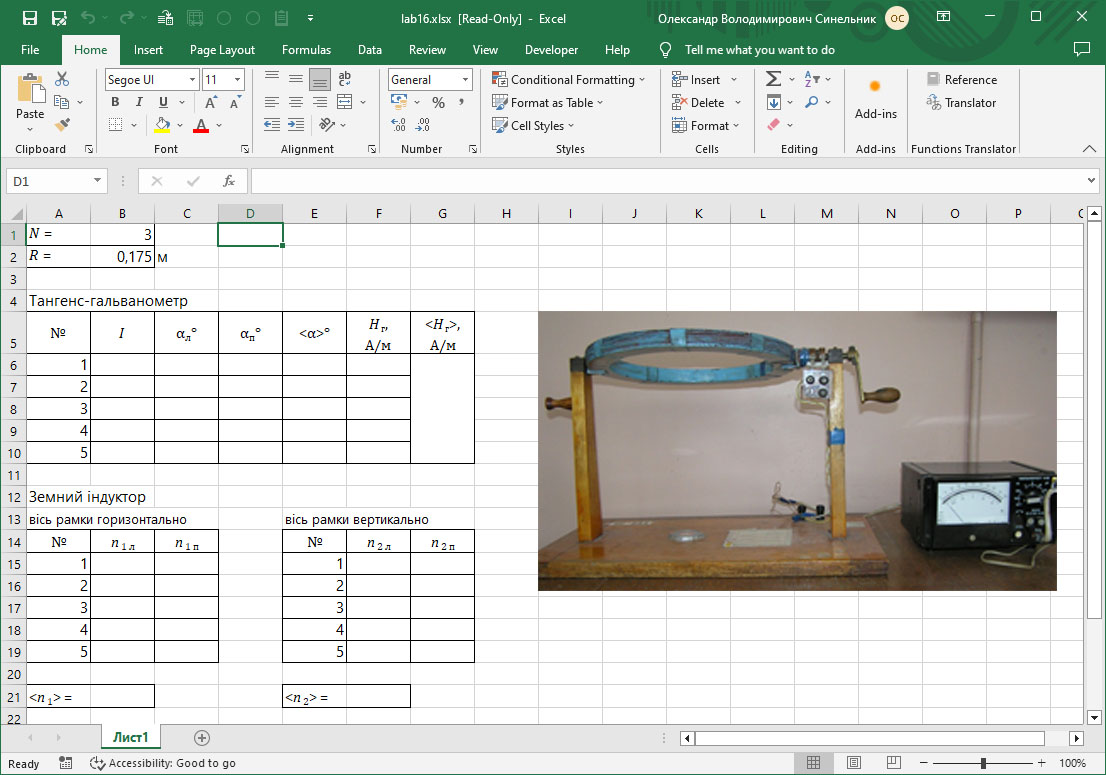
#1.8/23/24 Determination of elements of terrestrial magnetism
Experimental determination of the elements of terrestrial magnetism – the horizontal component of the magnetic field, the angles of magnetic inclination and magnetic declination.
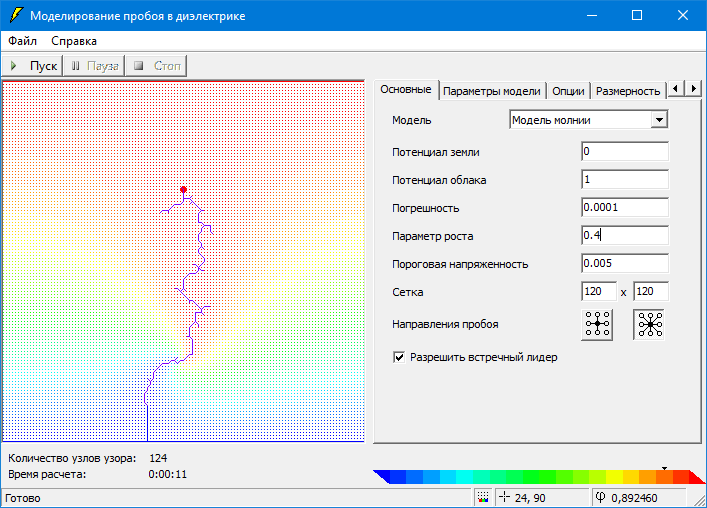
#1.12 Study of Dielectric breakdown
Study of the mechanism of dielectric breakdown in various media through computer modeling.
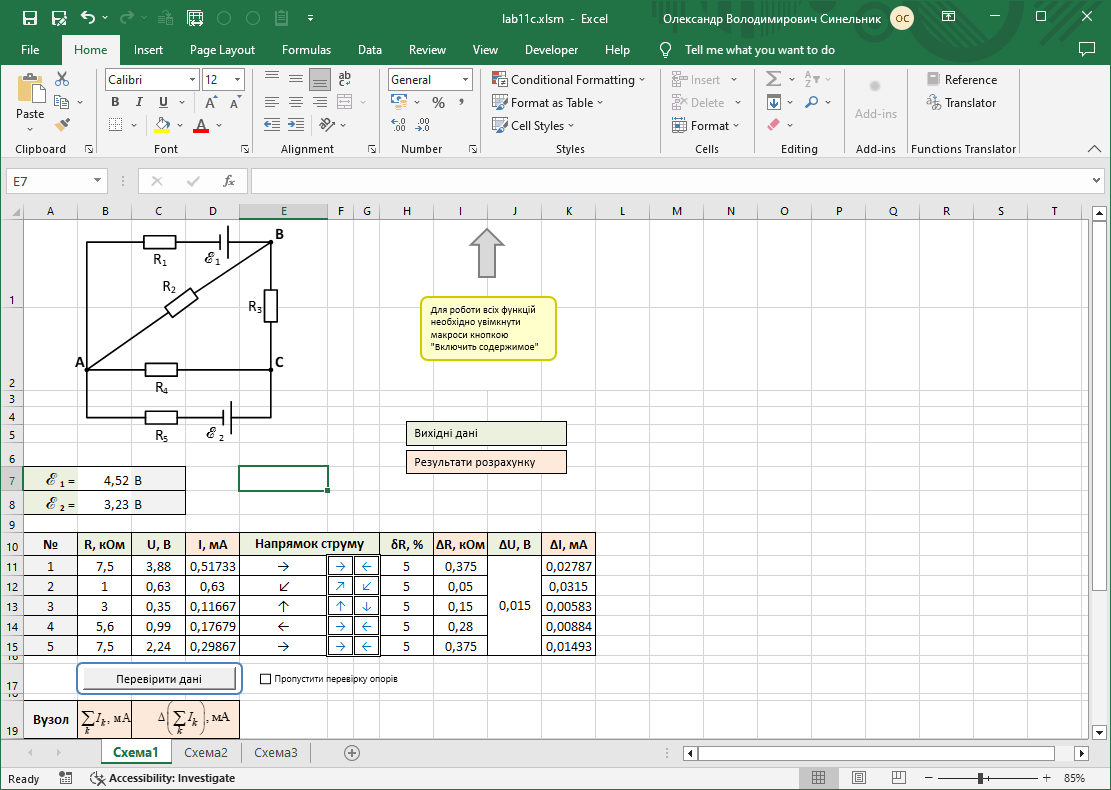
#20 Study of electric current flow in branched electrical circuits. Kirchhoff’s rules
Study of the laws of direct electric current flow in branched electrical circuits; experimental verification of Kirchhoff’s rules.
Oscillations and waves
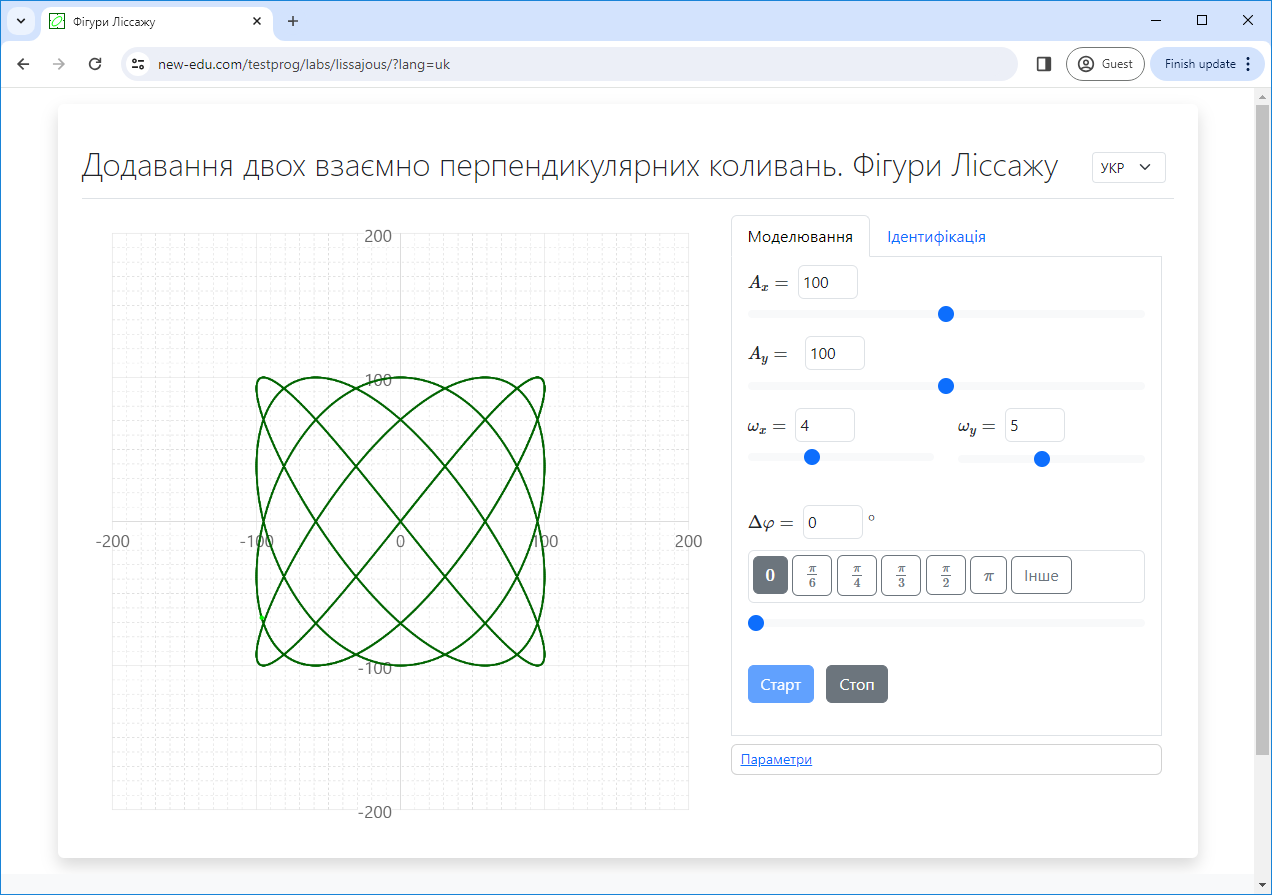
#2.6 Superposition of mutually perpendicular oscillations: Lissajous figures
Study of the dependence of the trajectory of motion of a point participating in two mutually perpendicular harmonic oscillations on the oscillation parameters.
#2.6* Determining the speed of sound in air by the method of adding mutually perpendicular oscillations
Determination of the speed of sound in air using a method based on the addition of mutually perpendicular vibrations using digital signal processing.
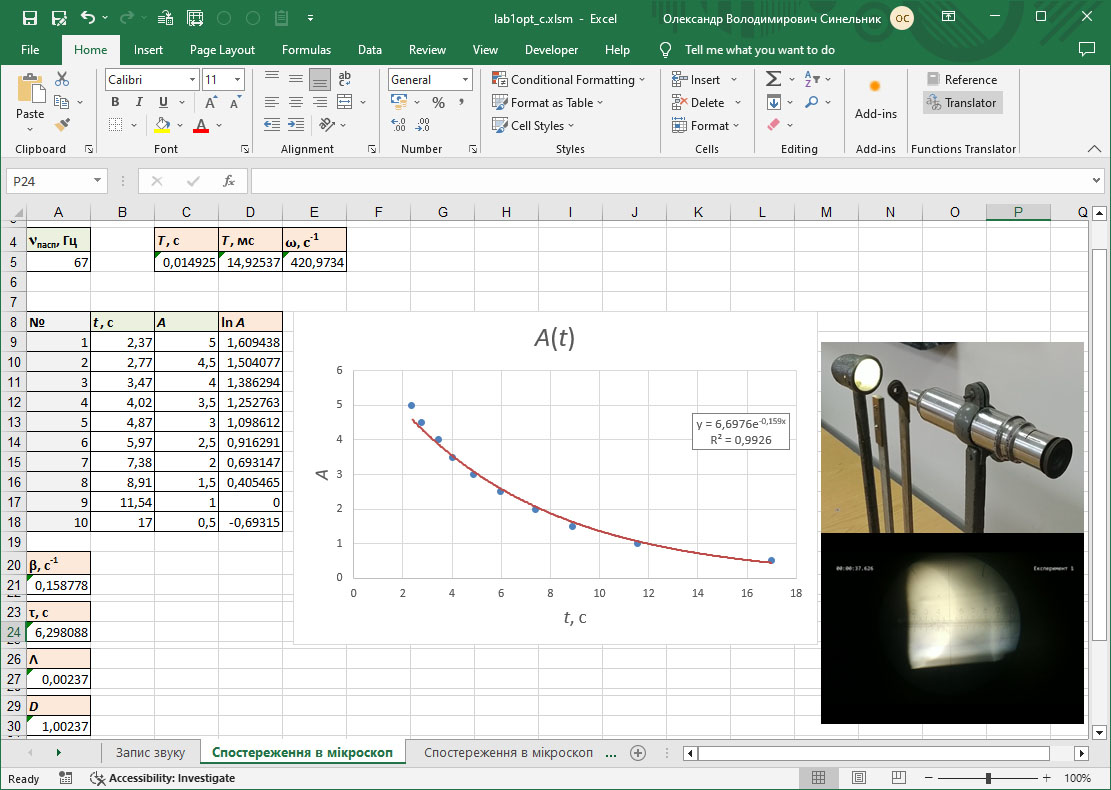
#2.10/12 Determination of acoustic parameters of a tuning fork by direct measurements of the amplitude of vibrations
Determination of the main parameters of tuning fork oscillations: linear frequency, cyclic frequency, period, decay decrement, logarithmic decay decrement, relaxation time, quality factor.
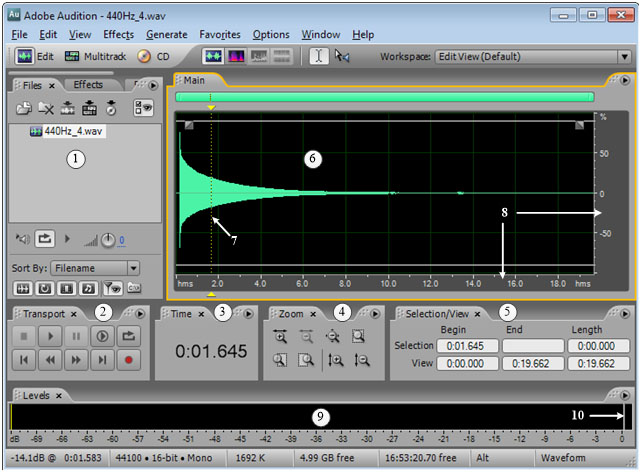
#2.10* Determination of acoustic parameters of a tuning fork by digital processing of sound recording
Determination of the main parameters of tuning fork oscillations: linear frequency, cyclic frequency, period, decay decrement, logarithmic decay decrement, relaxation time, quality factor.
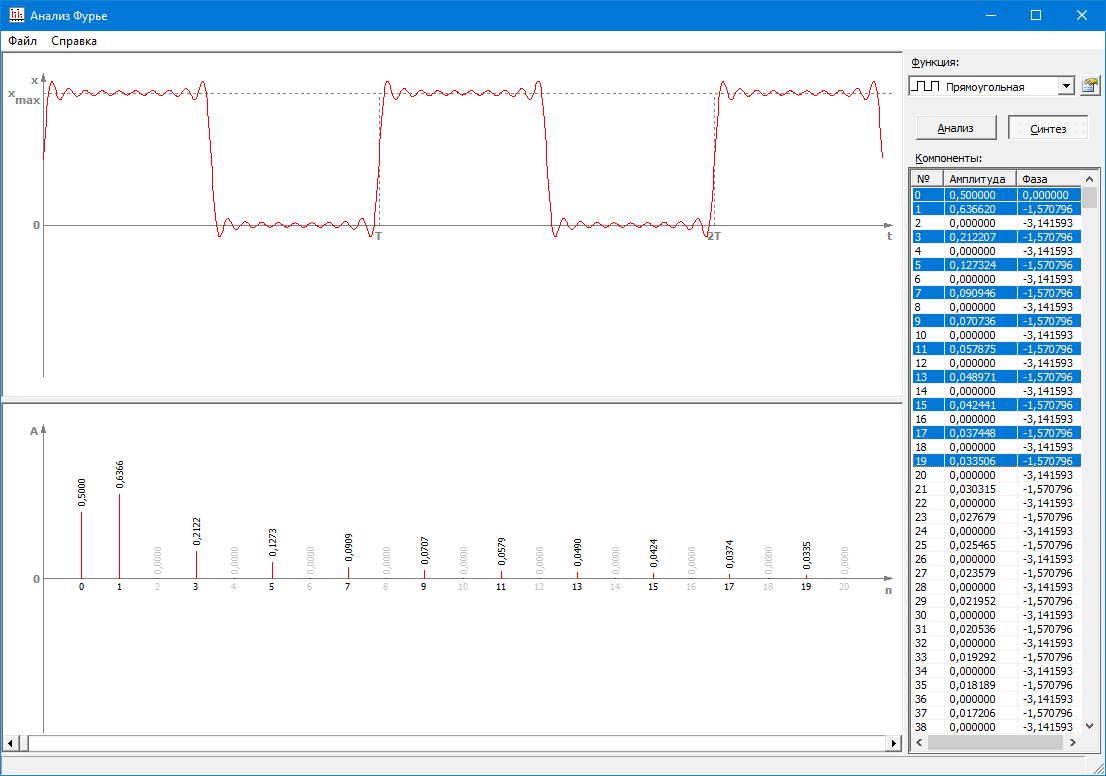
#2.11 Fourier analysis
Study of series and Fourier transforms and their use for spectral analysis of signals; reconstruction of a signal from its harmonic components.
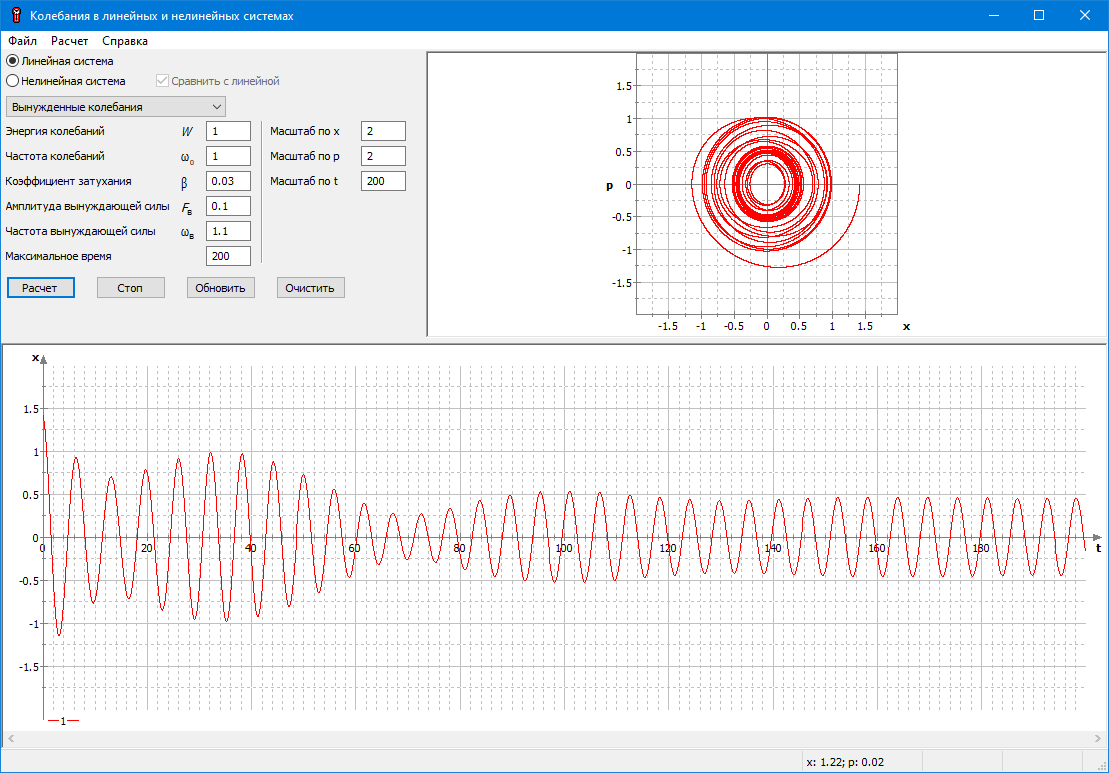
#2.9 Study of oscillations in linear and nonlinear systems
Study of the features of oscillatory processes in linear and nonlinear dynamic systems using the example of spring and mathematical pendulums. Study of the behavior of systems in cases of free, damped and forced oscillations. Introduction to the differences between linear and nonlinear oscillations, as well as methods of their analysis.
Optics
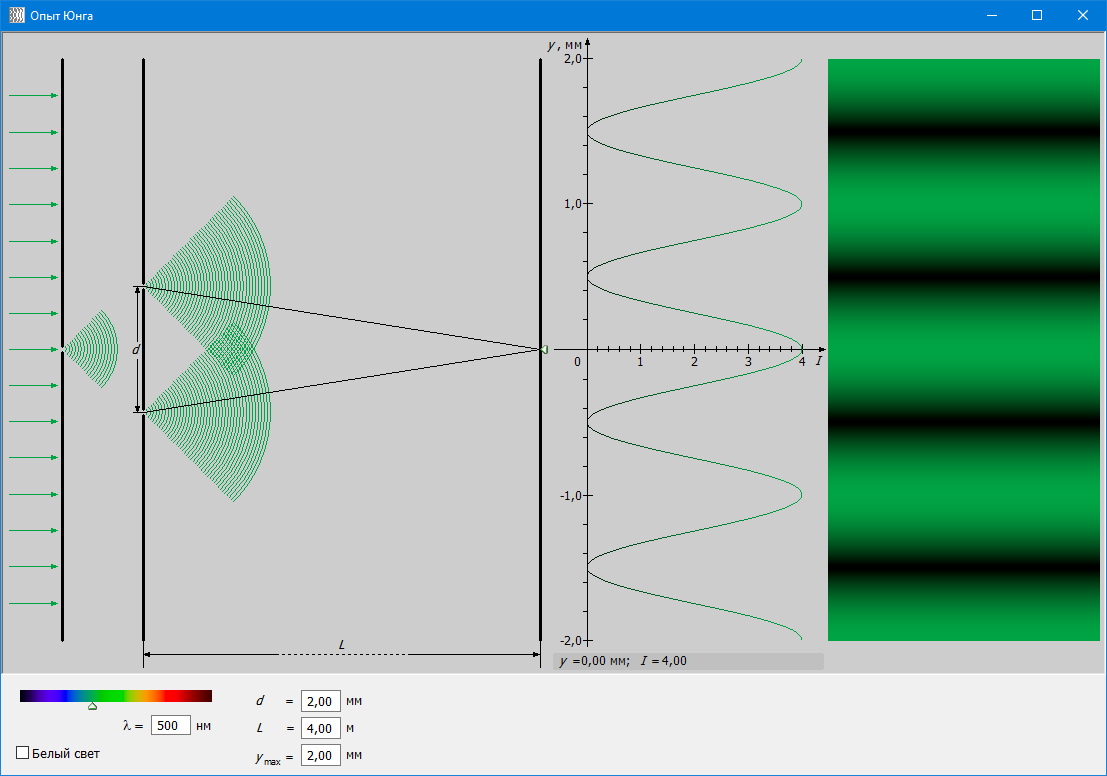
#2.2 Studying the phenomenon of interference: Young’s experiment
Study of the phenomenon of light interference using the example of Young’s experiment, study of the interference pattern obtained in Young’s experiment, study of the dependence of the location of interference maxima and minima on the wavelength of light and model parameters.
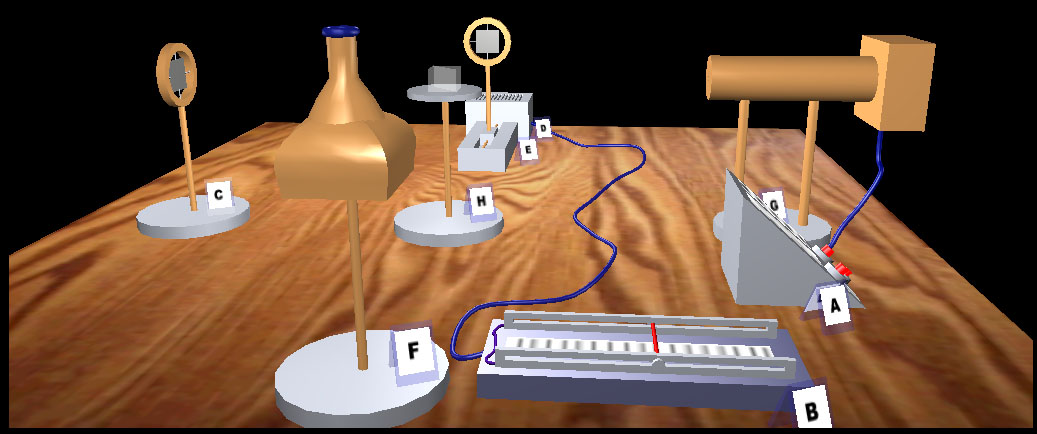
#2.3 Application of the Michelson interferometer to measure small displacements
The aim is to study the principle of operation of the Michelson interferometer and gain practical skills in using it to measure displacements.
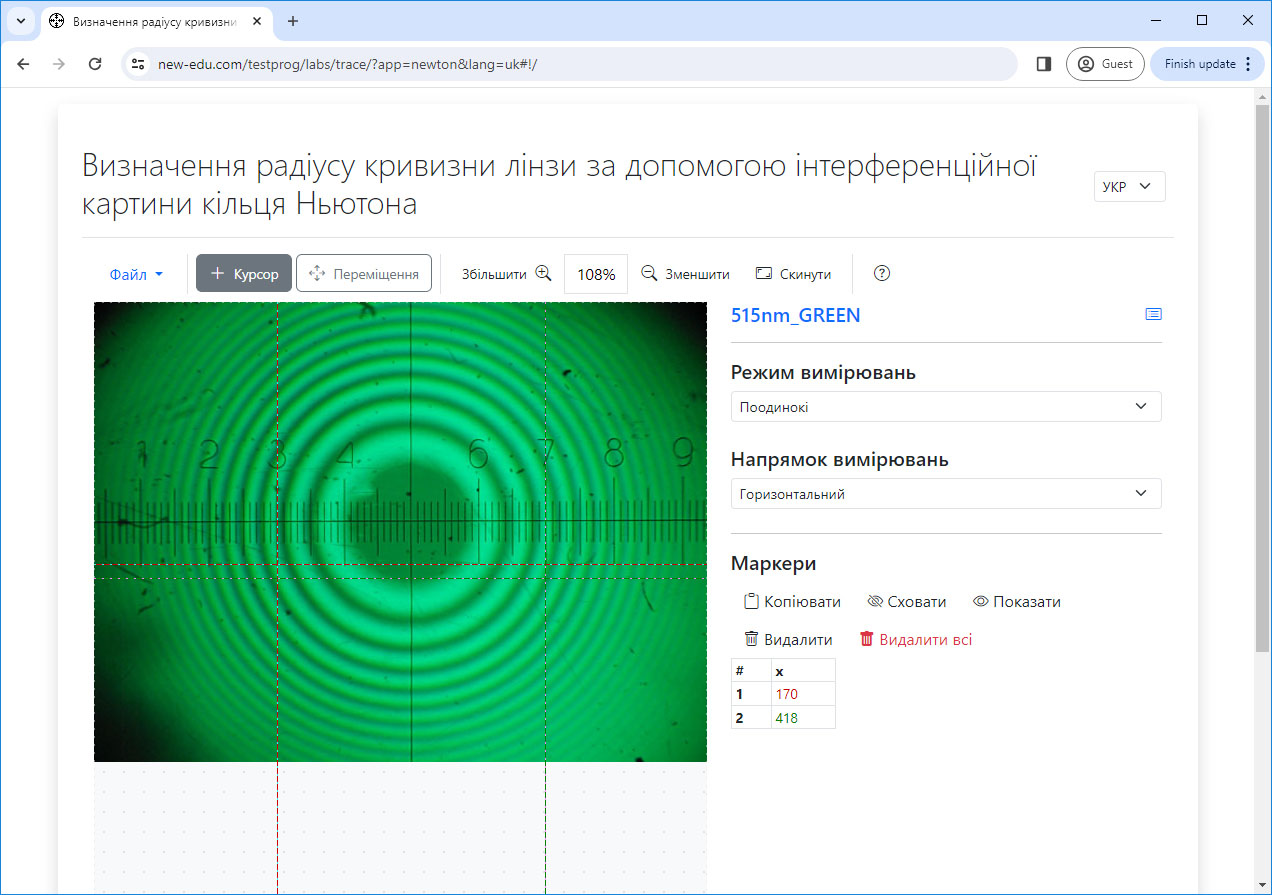
#2.4 Determining the radius of curvature of a lens using the interference pattern of Newton rings
Study of the phenomenon of interference, investigation of the regularities of the appearance of stripes of equal thickness, experimental determination of the radius of curvature of a lens using the interference pattern of Newton’s rings.
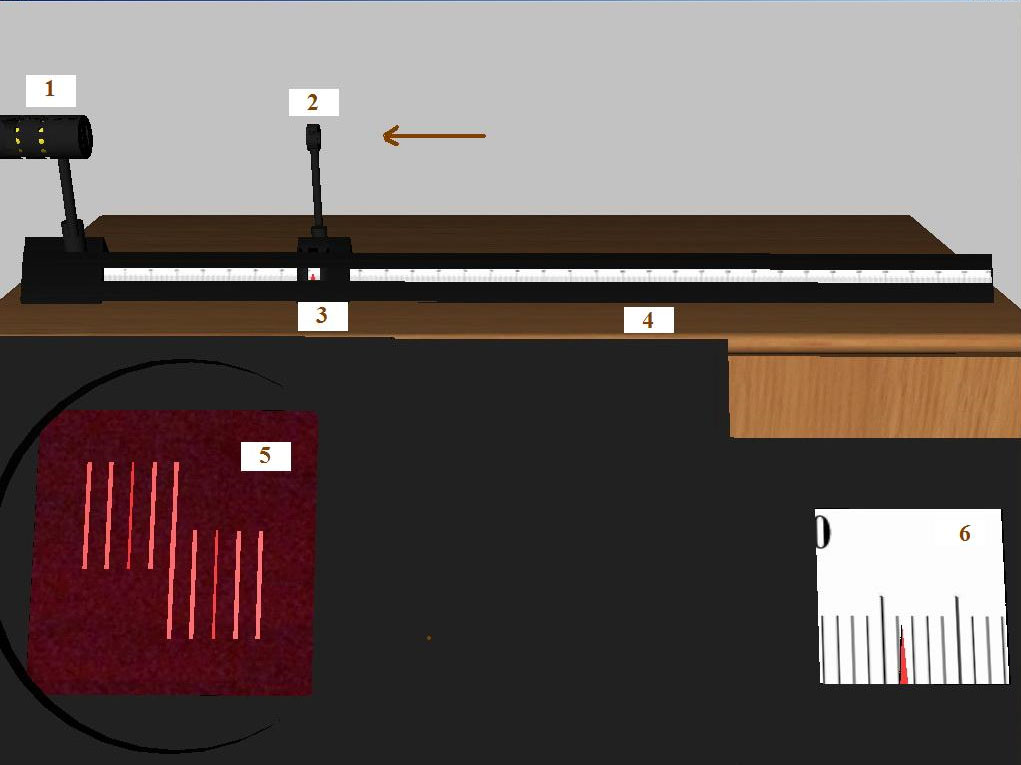
#2.5 Measuring the wavelength of light using diffraction grating
Determining the wavelength of monochromatic light using a diffraction grating and two slit-type light sources.
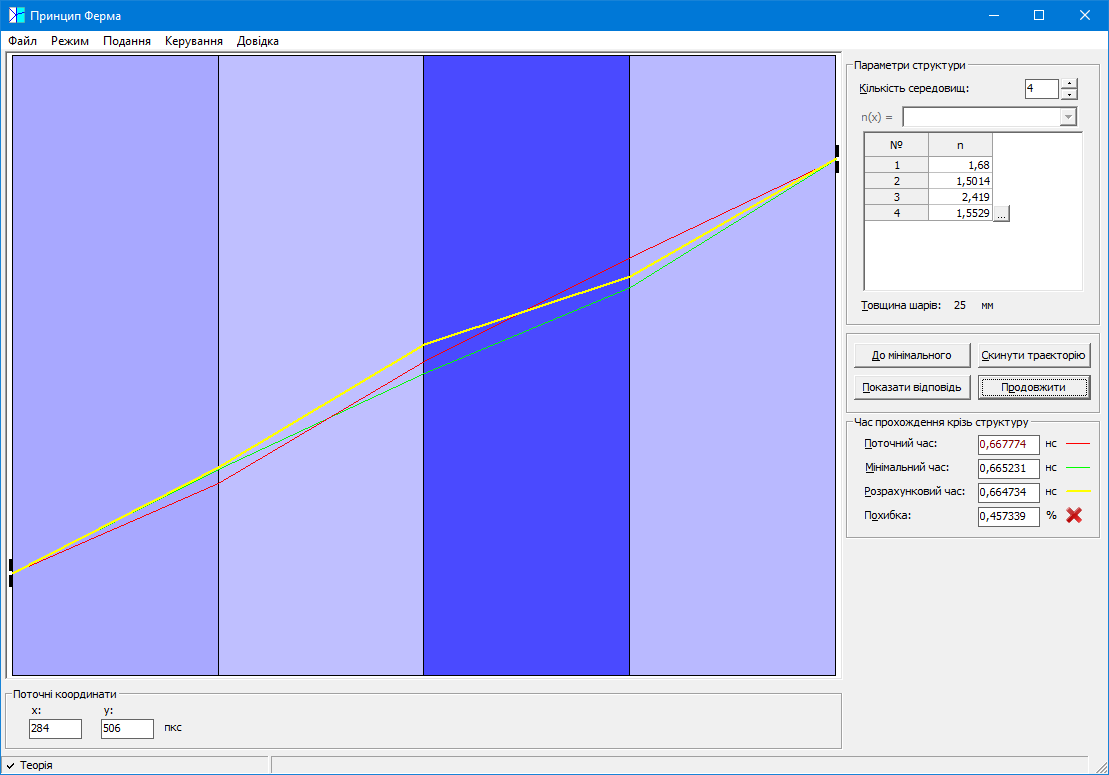
#2.7 Study of light transmission in layered media in the geometric optics approximation
Study of the laws of geometric optics using computer simulation of light propagation in inhomogeneous media.
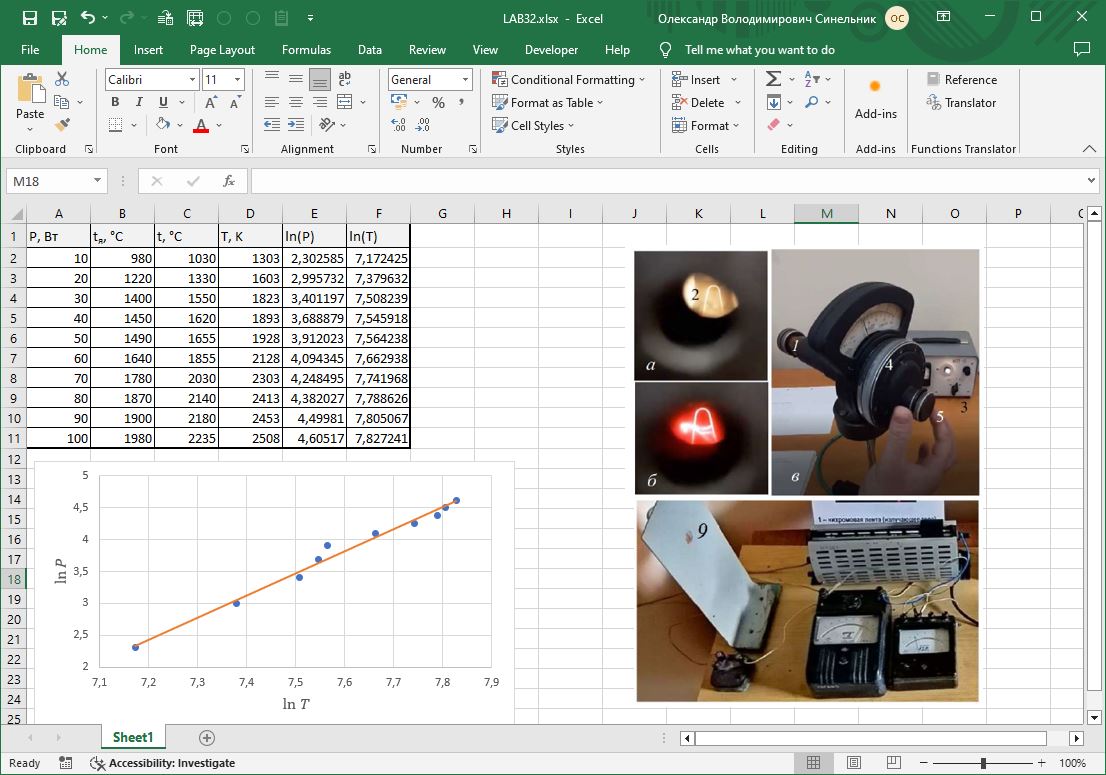
#32 Study of the laws of thermal radiation. Processing of the experimental results
Study of the laws of thermal radiation of bodies and determination of the Stefan–Boltzmann constant.
Atomic and nuclear physics
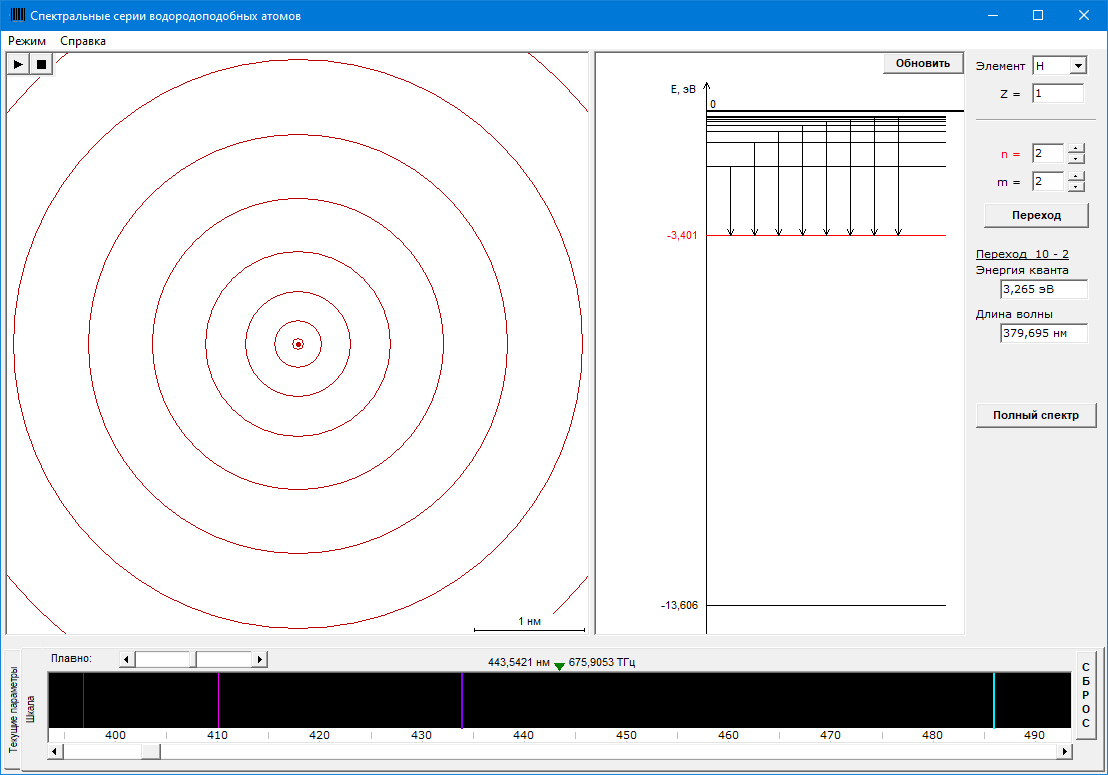
#3.1 Study of spectral series of radiation of hydrogen-like atoms
Study of the laws of radiation of hydrogen-like atoms.
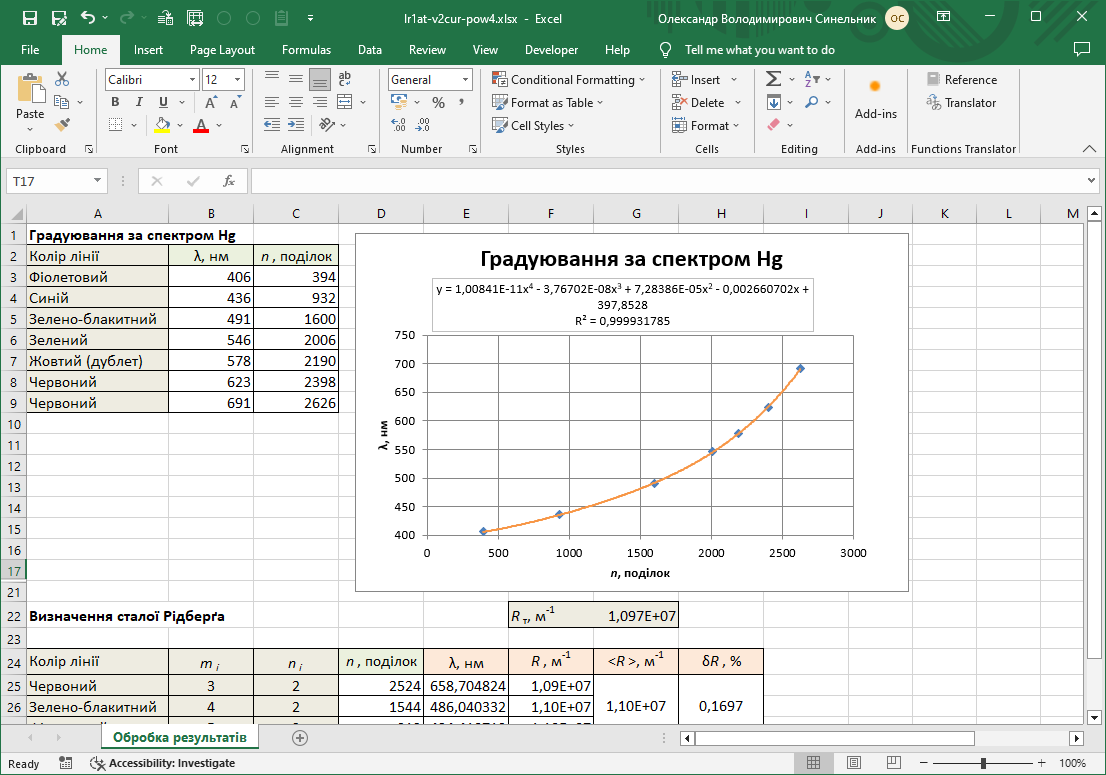
#3.1/34 Determination of the Rydberg constant. Processing of experimental results
Study of the atomic spectrum of hydrogen in the visible region and determination of the Rydberg constant.
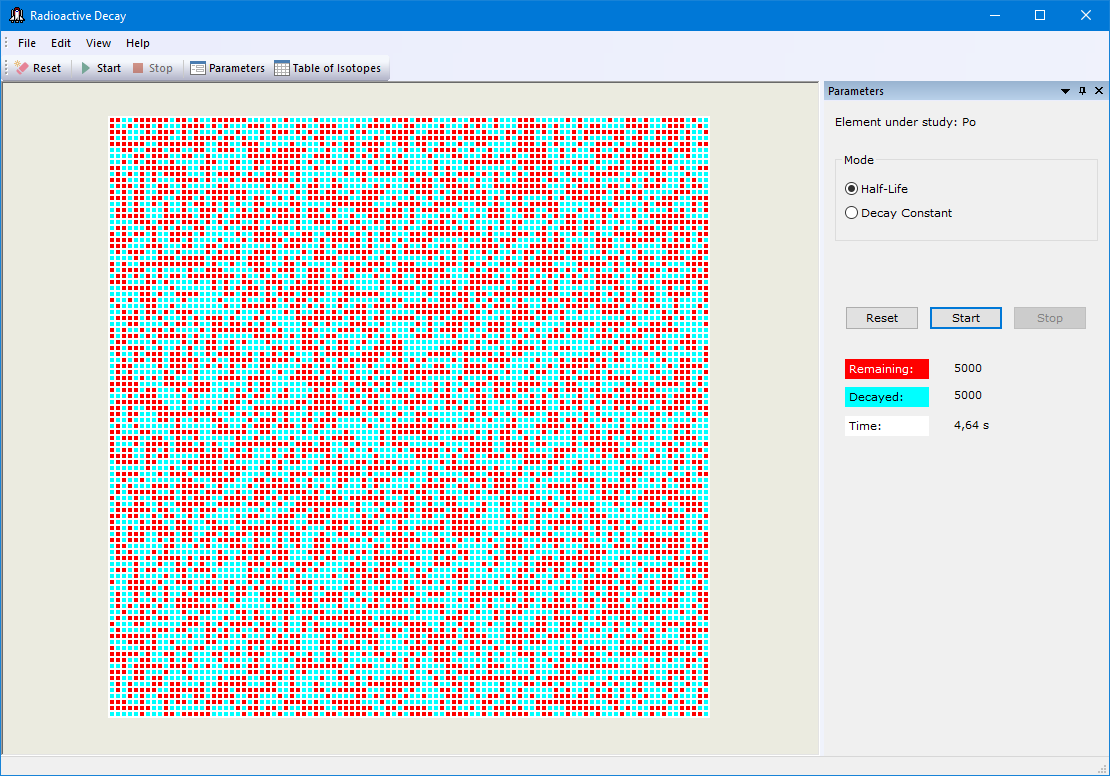
#3.4 Study of the law of radioactive decay
Study of the laws of radioactive decay through computer modeling; determination of the decay constant and half-life of a radionuclide.
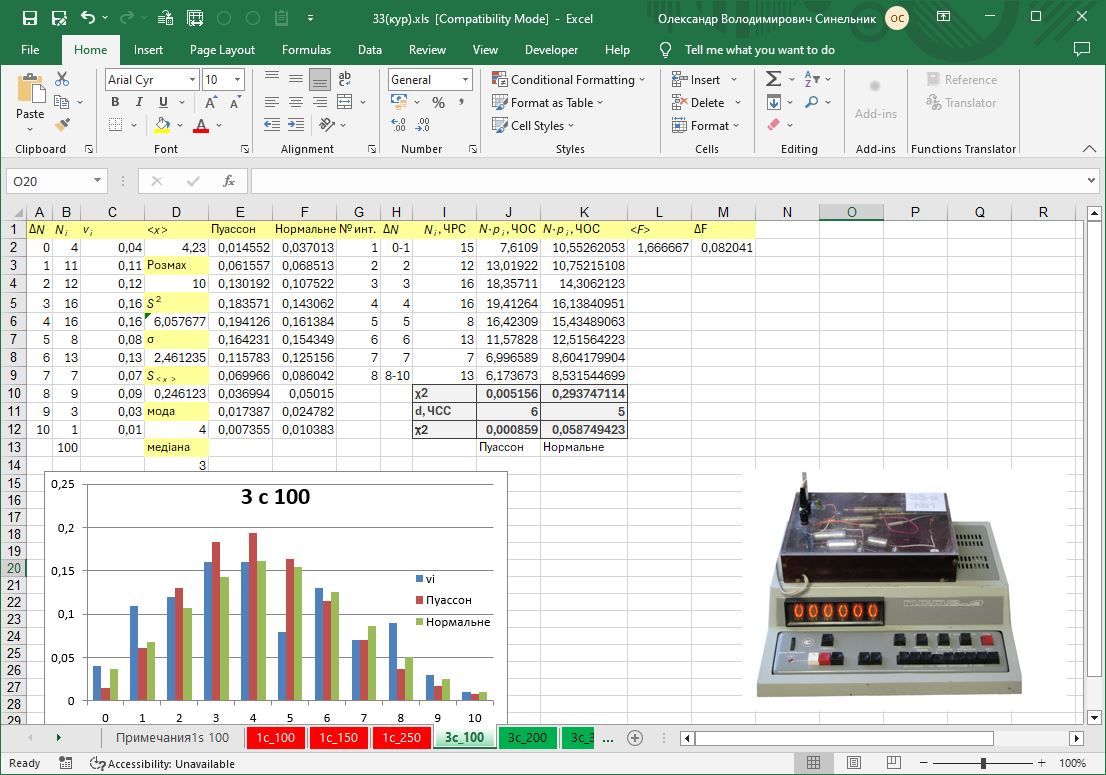
#3.5/42 Study of fluctuations in the radiation flux of the natural background radiation
Research into fluctuations in the flux of natural background radiation and the study of statistical patterns of random processes.
Quantum physics
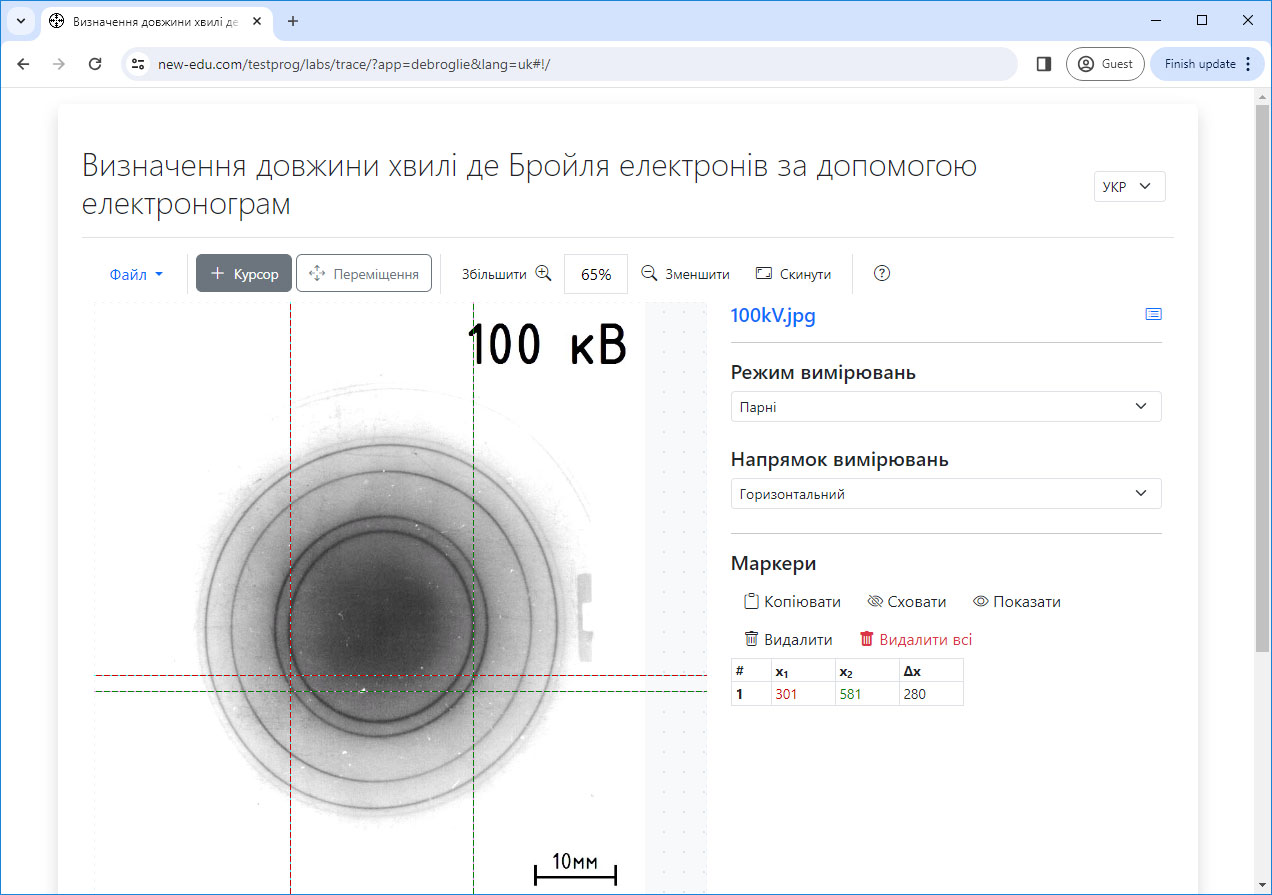
#3.2 Determining the de Broglie wavelength of electrons using electronogram
Determination of the de Broglie wavelength using electron diffraction patterns obtained by electron diffraction on crystalline substances.
Solid state physics
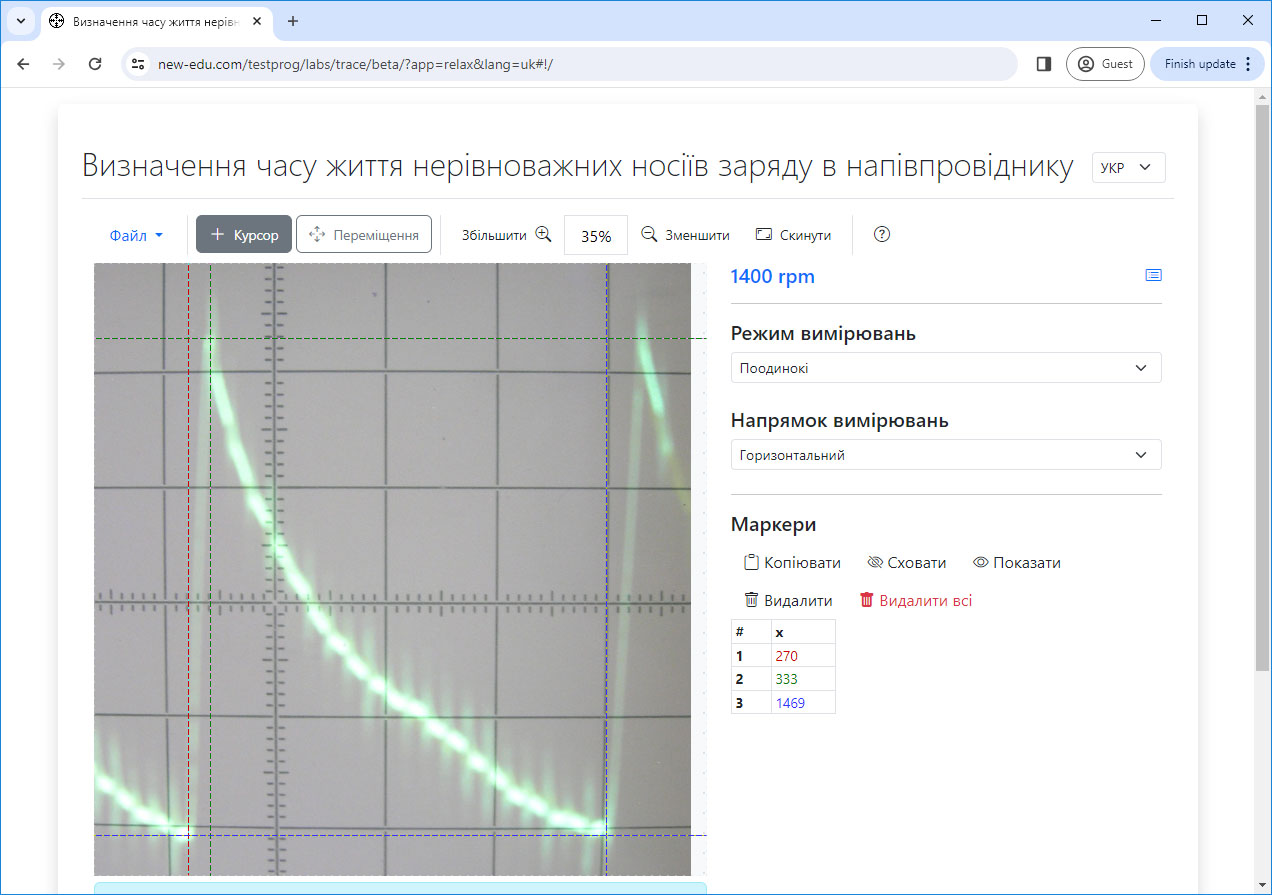
#3.3 Determination of the lifetime of non-equilibrium charge carriers in a semiconductor
Determination of the lifetime of non-equilibrium charge carriers from the photocurrent curve in a semiconductor versus time.
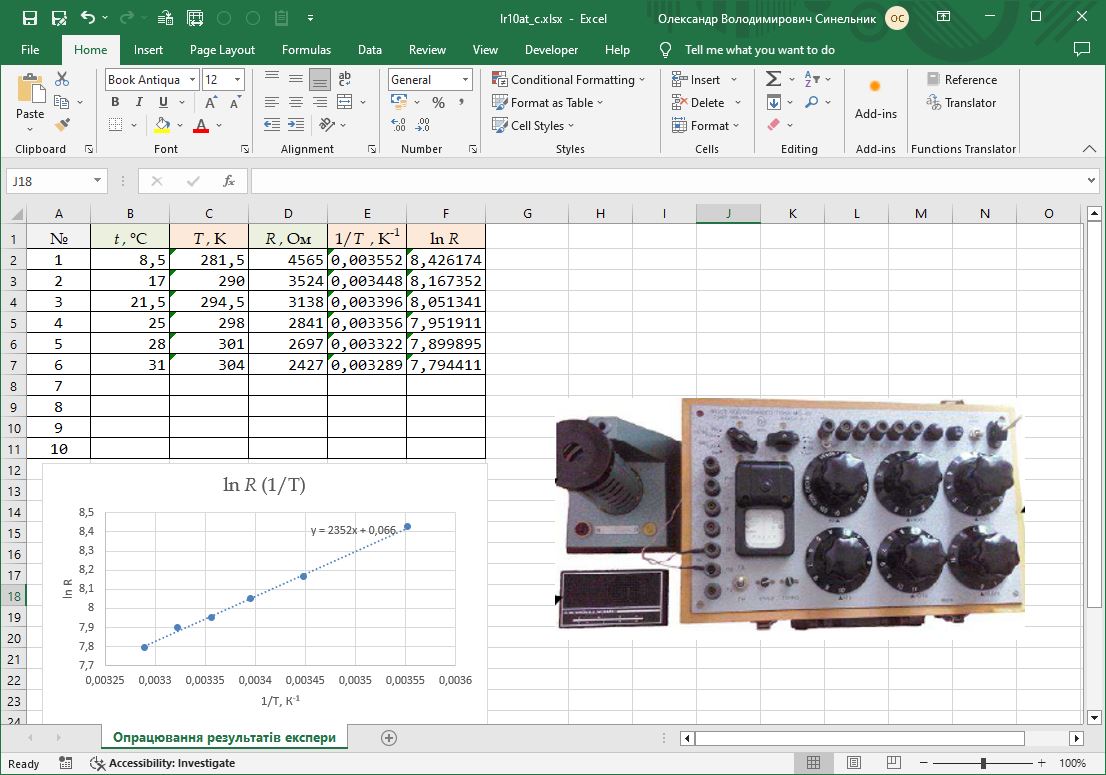
#38 Determination of the band gap of a semiconductor. Processing of experimental results
Determining the band gap of an intrinsic semiconductor.
General topics
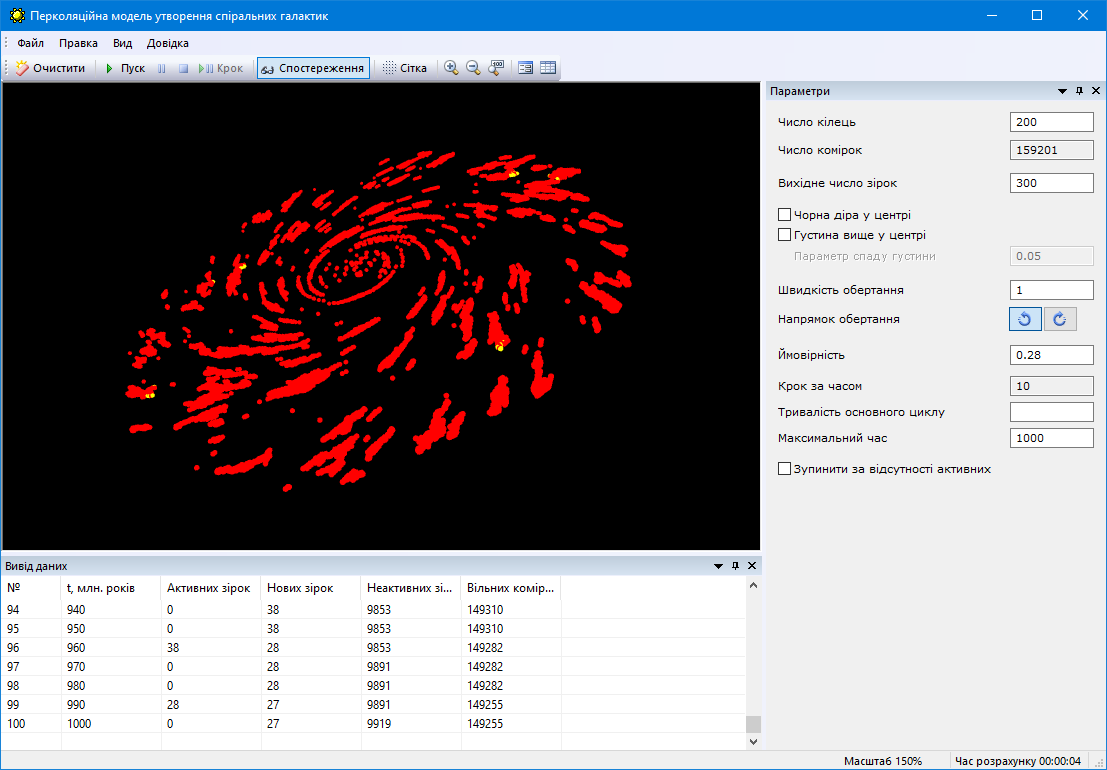
#3.6 Percolation model of spiral galaxy formation
Introduction to the concept of percolation, study of the patterns of spiral galaxy formation based on the percolation model.
Educational Software Suite “Computer Practicum”